730793
Silver, dispersion
nanoparticles, 20 nm particle size (TEM), 0.02 mg/mL in aqueous buffer, contains sodium citrate as stabilizer
Synonym(s):
Colloidal silver
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
nanoparticles
Quality Level
contains
sodium citrate as stabilizer
concentration
0.02 mg/mL in aqueous buffer
refractive index
n20/D 1.333
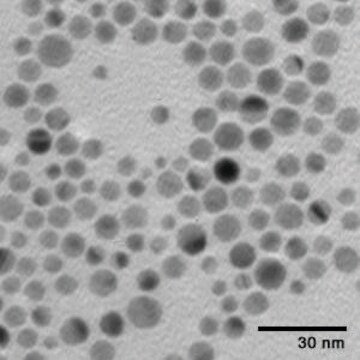
particle size
20 nm (TEM)
density
0.986 g/mL at 25 °C
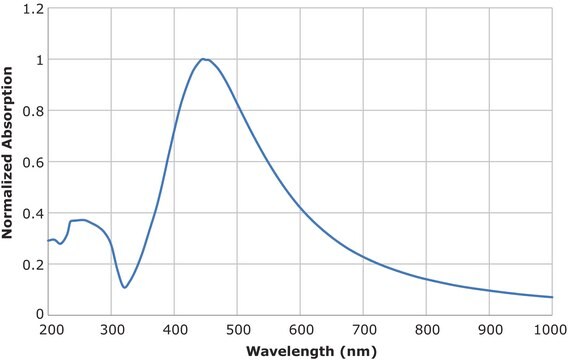
fluorescence
λem 401 nm FWHM 66 nm
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
[Ag]
InChI
1S/Ag
InChI key
BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- Surface-enhanced Raman analysis of sulfa drugs on colloidal silver dispersion.: This research explores the application of colloidal silver dispersion for the surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) analysis of sulfa drugs. The study demonstrates the potential of silver nanoparticles in enhancing Raman signals, making it a valuable technique for detecting and analyzing pharmaceuticals at low concentrations (Sutherland et al., 1990).
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
A key challenge for nanomaterial safety assessment is the ability to handle the large number of newly engineered nanomaterials (ENMs), including developing cost-effective methods that can be used for hazard screening.
Silver nanomaterials have unique physical, chemical, and optical properties that are currently being leveraged for a wide variety of biological applications.
Nanostructured Materials Through Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis
Nanostructured Materials Through Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service