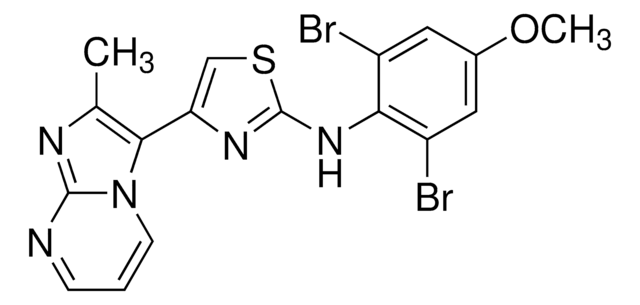
SML2971
K03861
≥98% (HPLC)
别名:
1-[4-(2-Aminopyrimidin-4-yloxy)phenyl]-3-[4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-3-trifluoromethylphenyl]urea, AUZ 454, AUZ-454, AUZ454, CCG 269702, CCG-269702, CCG269702, K 03861, K-03861, N-[4-[(2-Amino-4-pyrimidinyl)oxy]phenyl]-N′-[4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]urea
登录查看公司和协议定价
所有图片(1)
About This Item
推荐产品
品質等級
化驗
≥98% (HPLC)
形狀
powder
顏色
white to beige
溶解度
DMSO: 2 mg/mL, clear
儲存溫度
−20°C
SMILES 字串
FC(F)(F)c1c(ccc(c1)NC(=O)Nc3ccc(cc3)Oc4n[c]([nH]cc4)=N)CN2CCN(CC2)C
InChI
1S/C24H26F3N7O2/c1-33-10-12-34(13-11-33)15-16-2-3-18(14-20(16)24(25,26)27)31-23(35)30-17-4-6-19(7-5-17)36-21-8-9-29-22(28)32-21/h2-9,14H,10-13,15H2,1H3,(H2,28,29,32)(H2,30,31,35)
InChI 密鑰
PWDLXPJQFNVTNL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
生化/生理作用
ATP site-binding, cyclin-competitive, type II CDK2 inhibitor that selectively targets the DFG-out conformation.
K03861 is an ATP site-binding, cyclin-competitive, type II CDK2 inhibitor that selectively targets and locks the kinase in its inactive DFG-out conformation (CDK2 Kd = 50 nM, DFG-out stabilizing CDK2-C118L/A144C mutant Kd = 9.7 nM without vs. 134.1 nM with bound cycB; CDK2-C118L/A144C-cycA IC50 = 0.8 μM), rendering it incompatible for cyclin bining. K03861 selectively inhibits CDK2-C118L/A144C over CycA-bound wt CDK2 by in vitro kinase assay (IC50 = 0.8 vs. >10 μM) and inhibits the proliferation of immortalized multipotent otic progenitor (iMOP) murine cell line (by 81% and 92%, resepectively, at 0.1 and 1.0 μM).
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Carrow I Wells et al.
Nature communications, 11(1), 2743-2743 (2020-06-04)
Concerted multidisciplinary efforts have led to the development of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase inhibitors (CDKi's) as small molecule drugs and chemical probes of intracellular CDK function. However, conflicting data has been reported on the inhibitory potency of CDKi's and a systematic characterization
Atsushi Okuma et al.
Nature communications, 8(1), 2050-2050 (2017-12-14)
p16Ink4a and p21Cip1/Waf1 act as tumour suppressors through induction of cellular senescence. However, senescence-independent roles of these CDK inhibitors are not well understood. Here, we report an unexpected function of p16Ink4 and p21Cip1/Waf1, namely, tumour promotion through chemotaxis. In monocytic
Zhichao Song et al.
Stem cell reports, 9(5), 1516-1529 (2017-10-17)
Loss of spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs) significantly contributes to hearing loss. Otic progenitor cell transplantation is a potential strategy to replace lost SGNs. Understanding how key transcription factors promote SGN differentiation in otic progenitors accelerates efforts for replacement therapies. A
Zhichao Song et al.
Frontiers in cell and developmental biology, 7, 87-87 (2019-06-14)
Stem cell replacement therapy is a potential method for repopulating lost spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs) in the inner ear. Efficacy of cell replacement relies on proper differentiation. Defining the dynamic expression of different transcription factors essential for neuronal differentiation allows
Global Trade Item Number
| 货号 | GTIN |
|---|---|
| SML2971-25MG | 4065265405706 |
| SML2971-5MG | 4065265405713 |
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系客户支持