推荐产品
一般說明
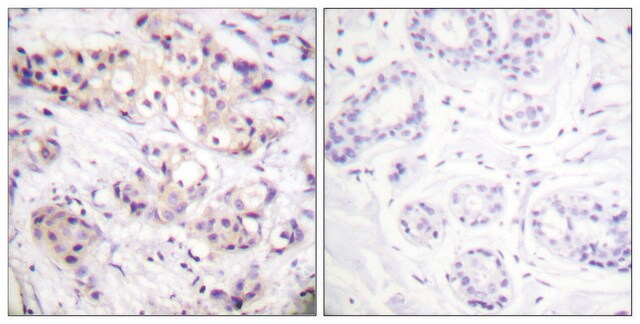
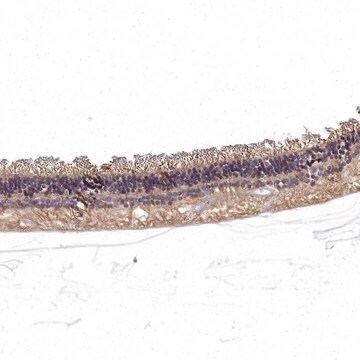
This gene encodes an extracellular protein that plays a crucial role in the cellular organization of the retina. The encoded protein is assembled and secreted from photoreceptors and bipolar cells as a homo-oligomeric protein complex. Mutations in this gene are responsible for X-linked retinoschisis, a common, early-onset macular degeneration in males that results in a splitting of the inner layers of the retina and severe loss in vision. (provided by RefSeq)
免疫原
RS1 (AAI41639.1, 1 a.a. ~ 224 a.a) full-length human protein.
Sequence
MSRKIEGFLLLLLFGYEATLGLSSTEDEGEDPWYQKACKCDCQGGPNALWSAGATSLDCIPECPYHKPLGFESGEVTPDQITCSNPEQYVGWYSSWTANKARLNSQGFGCAWLSKFQDSSQWLQIDLKEIKVISGILTQGRCDIDEWMTKYSVQYRTDERLNWIYYKDQTGNNRVFYGNSDRTSTVQNLLRPPIISRFIRLIPLGWHVRIAIRMELLECVSKCA
Sequence
MSRKIEGFLLLLLFGYEATLGLSSTEDEGEDPWYQKACKCDCQGGPNALWSAGATSLDCIPECPYHKPLGFESGEVTPDQITCSNPEQYVGWYSSWTANKARLNSQGFGCAWLSKFQDSSQWLQIDLKEIKVISGILTQGRCDIDEWMTKYSVQYRTDERLNWIYYKDQTGNNRVFYGNSDRTSTVQNLLRPPIISRFIRLIPLGWHVRIAIRMELLECVSKCA
生化/生理作用
RS1 (retinoschisin 1) is responsible for maintaining the structure of retina. Mutations in the gene cause X-Linked retinoschisis, which results in loss of vision.
外觀
Solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4
免責聲明
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Structural analysis of X-linked retinoschisis mutations reveals distinct classes which differentially effect retinoschisin function.
Ramsay EP
Human Molecular Genetics, 25(24), 5311-5320 (2016)
Ewan P Ramsay et al.
Human molecular genetics, 25(24), 5311-5320 (2016-11-01)
Retinoschisin, an octameric retinal-specific protein, is essential for retinal architecture with mutations causing X-linked retinoschisis (XLRS), a monogenic form of macular degeneration. Most XLRS-associated mutations cause intracellular retention, however a subset are secreted as octamers and the cause of their
Dario Marangoni et al.
Molecular therapy. Methods & clinical development, 5, 16011-16011 (2016-09-15)
X-linked retinoschisis (XLRS) is a retinal disease caused by mutations in the gene encoding the protein retinoschisin (RS1) and is one of the most common causes of macular degeneration in young men. Our therapeutic approach for XLRS is based on
Novel mutations of the RS1 gene in a cohort Chinese families with X-linked retinoschisis.
Chen J, et.al.
Molecular Vision, 20, 132-139 (2014)
Jieqiong Chen et al.
Molecular vision, 20, 132-139 (2014-02-08)
X-linked retinoschisis is a retinal dystrophy caused by mutations in the RS1 gene in Xp22.1. These mutations lead to schisis (splitting) of the neural retina and subsequent reduction in visual acuity in affected men (OMIM # 312700). The aim of
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门