所有图片(2)
About This Item
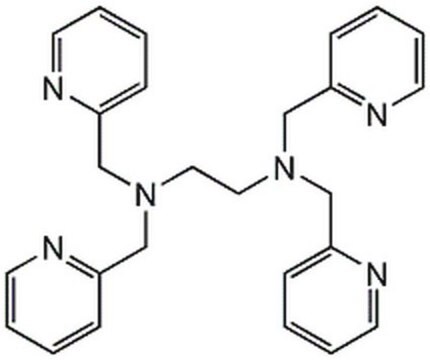
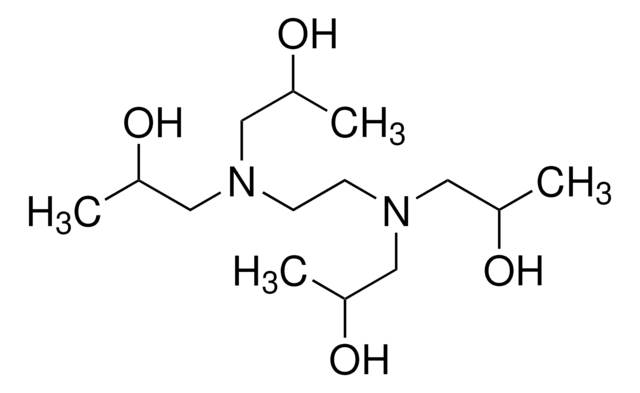
经验公式(希尔记法):
C26H28N6
CAS号:
分子量:
424.54
Beilstein:
4211982
MDL號碼:
分類程式碼代碼:
12352116
PubChem物質ID:
NACRES:
NA.77
推荐产品
product name
N,N,N′,N′-四(2-吡啶基甲基)乙二胺,
形狀
powder
SMILES 字串
C(CN(Cc1ccccn1)Cc2ccccn2)N(Cc3ccccn3)Cc4ccccn4
InChI
1S/C26H28N6/c1-5-13-27-23(9-1)19-31(20-24-10-2-6-14-28-24)17-18-32(21-25-11-3-7-15-29-25)22-26-12-4-8-16-30-26/h1-16H,17-22H2
InChI 密鑰
CVRXLMUYFMERMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
正在寻找类似产品? 访问 产品对比指南
應用
N,N,N′,N′-四(2-吡啶甲基)乙二胺用于:
- 处理人胚肾(HEK293T)细胞,评估其对Jembrana病病毒(JDV)病毒感染因子(Vif)功能的作用
- 在P19胚胎癌细胞中,螯合细胞凋亡过程中释放的锌离子
- 评估其对细胞慢病毒Vpx感染人单核THP-1细胞的作用
生化/生理作用
N,N,N′,N′-四(2-吡啶甲基)乙二胺(TPEN)通过抑制一氧化氮信号传导和Zn2+ 信号传导,引起人急性早幼粒细胞 NB4细胞中的促凋亡作用。在锌预处理的小胶质细胞中,TPEN抑制白介素6分泌和一氧化氮合酶(iNOS)mRNA表达。通过激活人结肠癌细胞中的ATM(毛细血管扩张性共济失调突变)和ATR(ATM-Rad3相关)信号传导,诱导DNA结构受损。
TPEN是一种可透过膜的锌螯合剂;可降低细胞内锌水平并诱导细胞凋亡(即细胞收缩和凋亡小体的形成、DNA片段化和形成典型的DNA梯状带)。
特點和優勢
该化合物是细胞凋亡研究的推荐产品。点击这里 发现更多精选的细胞凋亡产品。了解更多有关用于其他研究领域的生物活性小分子的信息,请访问 sigma.com/discover-bsm。
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
其他客户在看
Elodie Mattio et al.
Talanta, 183, 201-208 (2018-03-24)
In recent years, the development of 3D printing in flow analysis has allowed the creation of new systems with various applications. Up to now, 3D printing was mainly used for the manufacture of small units such as flow detection cells
Influence of extracellular zinc on M1 microglial activation
Higashi Y, et al.
Scientific Reports, 7(5), 43778-43778 (2017)
Synthesis of a highly Zn 2+-selective cyanine-based probe and its use for tracing endogenous zinc ions in cells and organisms
Guo Z, et al.
Nature Protocols, 9(6), 1245-1245 (2014)
Zinc depletion by TPEN induces apoptosis in human acute promyelocytic NB4 cells
Zhu B, et al.
Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 42(5), 1822-1836 (2017)
Nicholas Dietrich et al.
Nucleic acids research, 45(20), 11658-11672 (2017-10-05)
The essential element zinc plays critical roles in biology. High zinc homeostasis mechanisms are beginning to be defined in animals, but low zinc homeostasis is poorly characterized. We investigated low zinc homeostasis in Caenorhabditis elegans because the genome encodes 14
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门