推荐产品
产品名称
Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, for use in tissue culture media, DMSO solution
品質等級
形狀
DMSO solution
溶解度
water: soluble
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
正在寻找类似产品? 访问 产品对比指南
一般說明
蛋白酶抑制剂复合物混合多种抑制剂, 防止组织培养基中的分泌蛋白被蛋白酶降解。
蛋白酶抑制剂混合物处理以下细胞系48小时后无毒性:
A431、CHO、COS、HepG2和HeLa贴壁细胞系
Jurkat和HL-60悬浮细胞系
A431、CHO、COS、HepG2和HeLa贴壁细胞系
Jurkat和HL-60悬浮细胞系
特異性
抑制丝氨酸、半胱氨酸、和天冬氨酸蛋白酶和氨肽酶
應用
本品 专门针对组织培养基优化, 在培养基中作用48小时后可换新液,确保持续性 抑制蛋白酶。
蛋白酶抑制剂混合物的应用示例:
- 作为补充剂掺入上清液和裂解物,用于人精密切割肺切片(PCLS)的离体感染实验
- 用于抑制胰蛋白酶介导的蛋白水解,证明蛋白水解可恢复被蛋白冠抑制的纳米酶的催化活性
- 加入胰蛋白酶溶液用于胰蛋白酶抑制研究
- 作为放射性免疫沉淀分析(RIPA)缓冲液组分,裂解白细胞用于蛋白质印迹分析
生化/生理作用
蛋白酶抑制剂混合物专用于组织培养基。适合作为组织培养基添加剂,保护培养的组织分泌蛋白免遭降解。
特點和優勢
- 广泛的特异性
- 无毒性:作用48小时后,本品对贴壁细胞系A431、CHO、COS、HepG2和HeLa,以及悬浮细胞系Jurkat和HL-60无毒。
- 不含金属螯合剂:确保兼容下游应用
- 方便包装:1 mL玻璃瓶包装
- 易于使用:在组织培养基中以1:200或更高的稀释度使用,以防止分泌蛋白被蛋白酶水解。
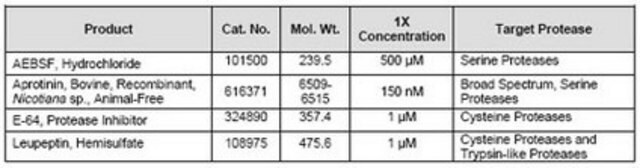
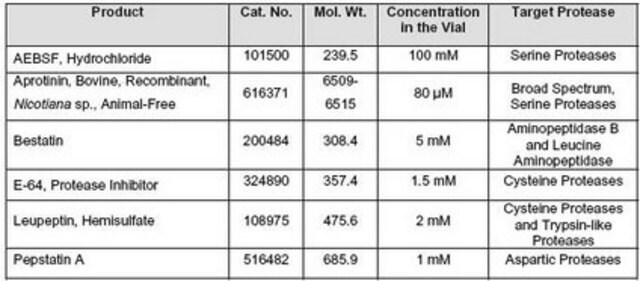
成分
抑肽酶
抑氨肽酶
E-64
亮肽素
胃蛋白酶抑制剂A
抑氨肽酶
E-64
亮肽素
胃蛋白酶抑制剂A
注意
孵育48小时后,产物对贴壁细胞系A431、CHO、COS、HepG2和HeLa,以及悬浮培养的Jurkat和HL-60细胞系无毒。
數量
在组织培养基中以1:200或更高的稀释度使用,以防止分泌蛋白的蛋白水解降解。
外觀
溶于DMSO中(D 2650,Hybri-Max)。
其他說明
仅供研发使用。&不可用于药物、家庭或其他用途。有关危险和安全处理方法的信息,请参阅安全数据说明书。
相關產品
产品编号
说明
价格
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
188.6 °F
閃點(°C)
87 °C
其他客户在看
Raymond L Warters et al.
Radiation research, 172(1), 82-95 (2009-07-08)
Although skin is usually exposed during human exposures to ionizing radiation, there have been no thorough examinations of the transcriptional response of skin fibroblasts and keratinocytes to radiation. The transcriptional response of quiescent primary fibroblasts and keratinocytes exposed to from
Takuma Shiratori et al.
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 200(1), 218-228 (2017-11-17)
As osteoclasts have the central roles in normal bone remodeling, it is ideal to regulate only the osteoclasts performing pathological bone destruction without affecting normal osteoclasts. Based on a hypothesis that pathological osteoclasts form under the pathological microenvironment of the
Matthew Townsend et al.
The Journal of physiology, 572(Pt 2), 477-492 (2006-02-14)
The accumulation of amyloid beta-protein (Abeta) in brain regions serving memory and cognition is a central pathogenic feature of Alzheimer's disease (AD). We have shown that small soluble oligomers of human Abeta that are naturally secreted by cultured cells inhibit
Vanessa Neuhaus et al.
PloS one, 8(8), e71728-e71728 (2013-08-24)
Annual outbreaks of influenza infections, caused by new influenza virus subtypes and high incidences of zoonosis, make seasonal influenza one of the most unpredictable and serious health threats worldwide. Currently available vaccines, though the main prevention strategy, can neither efficiently
Rachel Kaminsky et al.
Developmental cell, 17(5), 724-735 (2009-11-20)
Sumoylation is a reversible posttranslational modification that plays roles in many processes, including transcriptional regulation, cell division, chromosome integrity, and DNA damage response. Using a proteomics approach, we identified approximately 250 candidate targets of sumoylation in C. elegans. One such
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门