推荐产品
生物源
mouse
品質等級
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
ascites fluid
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
NN18, monoclonal
分子量
antigen 160 kDa
包含
15 mM sodium azide
物種活性
human, pig
技術
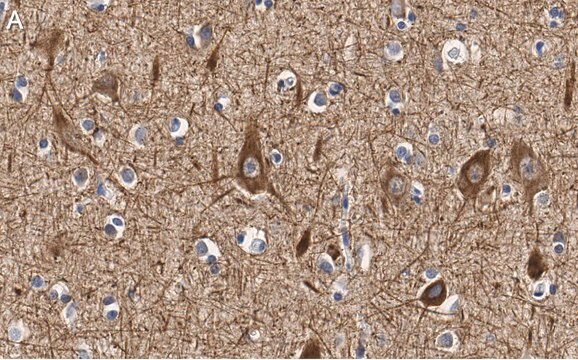
immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections): 1:40 using human tissue sections
immunohistochemistry (frozen sections): suitable
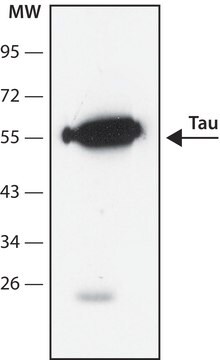
western blot: suitable
同型
IgG1
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
chicken ... NEFM(396206)
human ... NEFM(4741)
mouse ... Nefm(18040)
rat ... Nefm(24588)
一般說明
Monoclonal Anti-Neurofilament 160 (mouse IgG1 iso-type) is produced by the fusion mouse myeloma cells and splenocytes from an immunized mouse. Neurofilaments are composed of three sub-units- light NFL protein, medium NFM protein, heavy NFH protein. Along with there two other intermediate filaments are present α-internexin and peripherin. Neurofilaments are phosphoproteins.
Neurofilaments belong to the intermediate filament family and are expressed mainly in cells or tissues of neuronal origin. It is crucial for proper radial growth of axons.
特異性
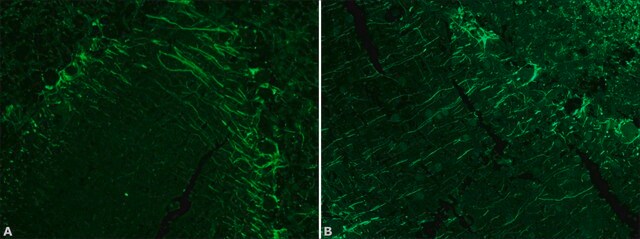
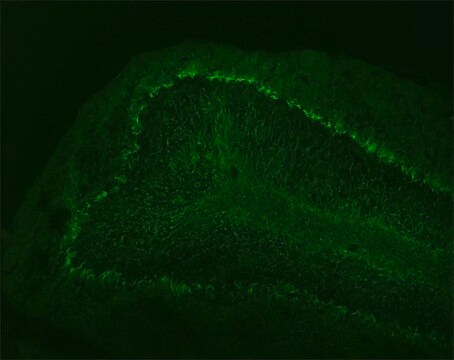
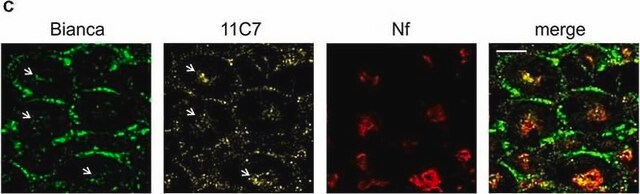
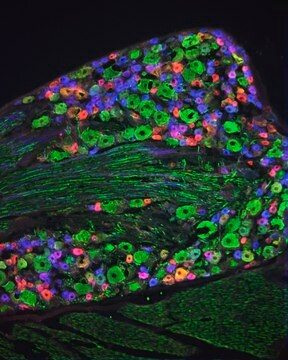
Mouse monoclonal anti-neurofilament 160 antibody reacts specifically with neurofilaments of molecular weight 160,000 but does not cross react with other intermediate filament proteins.
免疫原
neurofilaments from pig spinal cord.
應用
Monoclonal anti-neurofilament 160 antibody (diluted 1: 5000) can be used as internal loading controls in immunoblotting. It can also be used in whole-mount immunohistochemistry and western blot. Monoclonal anti-neurofilament 160 antibodies can be used for localization of neurofilaments of molecular weight 160,000 in cultured cells or tissues preparation.
Monoclonal anti-neurofilament 160 antibody has been used in
- Immunoblotting.
- Immunohistochemistry
- Immunofluorescence
生化/生理作用
Neurofilaments play a role in axonal calibre as they help in movement of an impulse down the axon. Their activity depends on phosphorylation of neurofilaments.Mutations of neurofilaments causes Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease. Accumulation of neurofilaments has been observed in many human neurological diseases like Alzheimer′s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, diabetic neuropathy, and giant axonal neuropathy.
免責聲明
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
其他客户在看
F Maina et al.
Genes & development, 11(24), 3341-3350 (1998-02-07)
The development of the nervous system is a dynamic process during which factors act in an instructive fashion to direct the differentiation and survival of neurons, and to induce axonal outgrowth, guidance to, and terminal branching within the target tissue.
Svetlana Gorokhova et al.
PLoS genetics, 10(2), e1004081-e1004081 (2014-02-12)
Neurotrophins and their receptors control a number of cellular processes, such as survival, gene expression and axonal growth, by activating multiple signalling pathways in peripheral neurons. Whether each of these pathways controls a distinct developmental process remains unknown. Here we
M K Lee et al.
Current opinion in cell biology, 6(1), 34-40 (1994-02-01)
Neurofilaments make up the major intermediate filament system in mature neurons. Recent studies demonstrate that neurofilaments in vivo are obligate heteropolymers and are required for proper radial growth of axons. Furthermore, forced over-expression of neurofilament subunits in transgenic mice shows
Yibo Qu et al.
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 30(28), 9392-9401 (2010-07-16)
During hindbrain development, facial branchiomotor neurons (FBM neurons) migrate from medial rhombomere (r) 4 to lateral r6. In zebrafish, mutations in planar cell polarity genes celsr2 and frizzled3a block caudal migration of FBM neurons. Here, we investigated the role of
Grzegorz Wicher et al.
Journal of neurotrauma, 34(22), 3173-3182 (2017-05-12)
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a devastating condition, often leading to life-long consequences for patients. Even though modern neurointensive care has improved functional and cognitive outcomes, efficient pharmacological therapies are still lacking. Targeting peripherally derived, or resident inflammatory, cells that
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门