推荐产品
重組細胞
expressed in E. coli
形狀
solution
enzyme activity
≥20 units/mg protein
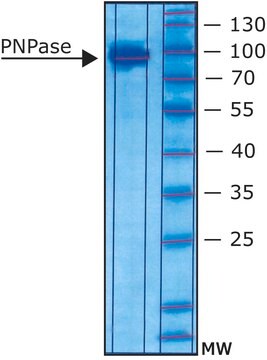
分子量
~90 kDa
濃度
400-600 μg/mL protein
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−70°C
生化/生理作用
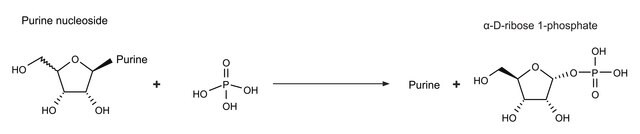
Polynucleotide phosphorylase (PNPase) is a bifunctional enzyme with a phosphorolytic 3′ to 5′ exoribonuclease activity and a 3′-terminal oligonucleotide polymerase activity. It is also involved in mRNA processing and degradation in bacteria, plants, and humans.
外觀
supplied as a solution in 20 mM HEPES buffer, pH 7.9, with 0.1 mM EDTA, 2 mM DTT, 12.5 mM MgCl2, ~130 mM KCl, and 20% (w/v) glycerol.
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Lukasz S Borowski et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1797(6-7), 1066-1070 (2010-02-02)
Protein complexes responsible for RNA degradation play important role in three key aspects of RNA metabolism: they control stability of physiologically functional transcripts, remove the unnecessary RNA processing intermediates and destroy aberrantly formed RNAs. In mitochondria the post-transcriptional events seem
Victoria Portnoy et al.
RNA (New York, N.Y.), 14(2), 297-309 (2007-12-18)
PNPase is a major exoribonuclease that plays an important role in the degradation, processing, and polyadenylation of RNA in prokaryotes and organelles. This phosphorolytic processive enzyme uses inorganic phosphate and nucleotide diphosphate for degradation and polymerization activities, respectively. Its structure
Hsiao-Wen Chen et al.
Molecular and cellular biology, 26(22), 8475-8487 (2006-09-13)
We recently identified polynucleotide phosphorylase (PNPase) as a potential binding partner for the TCL1 oncoprotein. Mammalian PNPase exhibits exoribonuclease and poly(A) polymerase activities, and PNPase overexpression inhibits cell growth, induces apoptosis, and stimulates proinflammatory cytokine production. A physiologic connection for
Takashi Nagaike et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 280(20), 19721-19727 (2005-03-17)
Mammalian mitochondrial (mt) mRNAs have short poly(A) tails at their 3' termini that are post-transcriptionally synthesized by mt poly(A) polymerase (PAP). The polyadenylation of mt mRNAs is known to be a key process needed to create UAA stop codons that
Magdalena Leszczyniecka et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99(26), 16636-16641 (2002-12-11)
Terminal differentiation and cellular senescence display common properties including irreversible growth arrest. To define the molecular and ultimately the biochemical basis of the complex physiological changes associated with terminal differentiation and senescence, an overlapping-pathway screen was used to identify genes
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门