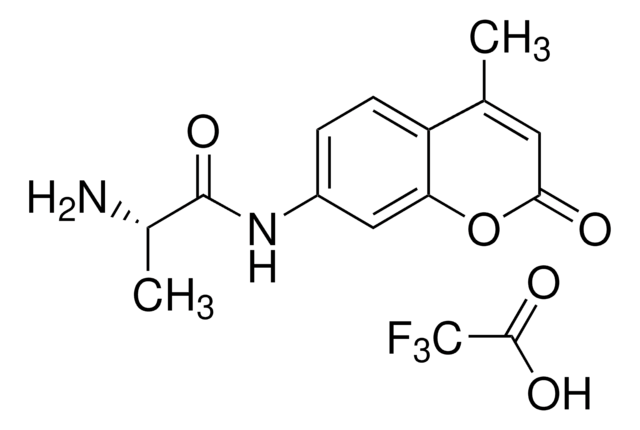
A1057
L-Aspartic acid β-(7-amido-4-methylcoumarin)
≥98%, suitable for ligand binding assays
别名:
L-Aspartic acid β-(4-methyl-7-coumarinylamide), L-Aspartic acid 4-(4-methyl-7-coumarinylamide)
登录查看公司和协议定价
所有图片(1)
About This Item
经验公式(希尔记法):
C14H14N2O5
CAS号:
分子量:
290.27
MDL號碼:
分類程式碼代碼:
12352209
PubChem物質ID:
NACRES:
NA.26
推荐产品
产品名称
L-Aspartic acid β-(7-amido-4-methylcoumarin), fluorescent amino acid
品質等級
化驗
≥98%
形狀
powder
技術
ligand binding assay: suitable
顏色
white to off-white
儲存溫度
−20°C
SMILES 字串
CC1=CC(=O)Oc2cc(NC(=O)C[C@H](N)C(O)=O)ccc12
InChI
1S/C14H14N2O5/c1-7-4-13(18)21-11-5-8(2-3-9(7)11)16-12(17)6-10(15)14(19)20/h2-5,10H,6,15H2,1H3,(H,16,17)(H,19,20)/t10-/m0/s1
InChI 密鑰
ARZPQBJTLVVDNP-JTQLQIEISA-N
正在寻找类似产品? 访问 产品对比指南
生化/生理作用
L-Aspartic acid β-(7-amido-4-methylcoumarin) is used as a fluorogenic substrate for studying the specificity and kinetics of lysosomal glycoasparaginase(s) (aspartylglucosaminidase) and L-asparaginase(s).
L-Aspartic acid-β-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin is sensitive and specific fluorogenic substrate used to assay for lysosomal glycoasparaginase (aspartylglucosaminidase) activity and the diagnosis of aspartylglucosaminuria.
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Voznyi YaV et al.
Journal of inherited metabolic disease, 16(6), 929-934 (1993-01-01)
L-Aspartic acid-beta-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin is a sensitive and specific fluorogenic substrate for lysosomal glycoasparaginase (aspartylglucosaminidase). Fibroblasts and leukocytes from 8 patients with aspartylglucosaminuria, showed 1-7% of the mean normal glycoasparaginase activity. Heterozygotes showed intermediate activities. Glycoasparaginase activity in chorionic villi, cultured trophoblasts
P Ylikangas et al.
Analytical biochemistry, 280(1), 42-45 (2000-05-11)
The antineoplastic enzyme L-asparaginase is commonly used for the induction of remission in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). There is no simple method available for measuring the activity of this highly toxic drug. We incubated L-asparaginase from Erwinia chrysanthemi with L-aspartic
I Mononen et al.
Clinical chemistry, 40(3), 385-388 (1994-03-01)
Serum, plasma, and lymphocytes from aspartylglycosaminuria (AGU) patients and carriers and from normal controls were incubated with a fluorescent glycosylasparaginase substrate, L-aspartic acid beta-(7-amido-4-methylcoumarin), and the release of 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin was measured fluorometrically after incubation for 1-4 h. The mean glycosylasparaginase
I T Mononen et al.
Analytical biochemistry, 208(2), 372-374 (1993-02-01)
Recent experimental work on the mechanism of action of glycosylasparaginase suggests that the enzyme specifically reacts toward the L-asparagine or L-aspartic acid moiety of its substrates. Based on this, a new sensitive assay for glycosylasparaginase activity has been developed using
Seiji Saito et al.
Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 377(4), 1168-1172 (2008-11-11)
To elucidate the basis of aspartylglucosaminuria (AGU) from the viewpoint of enzyme structure, we constructed structural models of mutant aspartylglucosaminidase (AGA) proteins using molecular modeling software, TINKER. We classified the amino acid substitutions responsible for AGU and divided them into
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门