所有图片(1)
About This Item
经验公式(希尔记法):
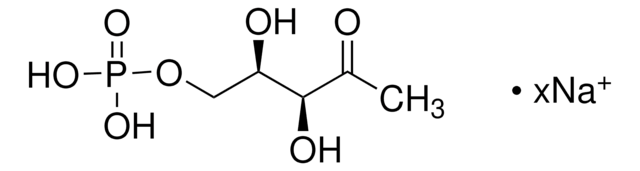
C5H11O7P · xLi+
CAS号:
分子量:
214.11 (free acid basis)
分類程式碼代碼:
12352106
PubChem物質ID:
NACRES:
NA.25
推荐产品
化驗
≥98% (TLC)
儲存溫度
−20°C
SMILES 字串
O=P(O)(O)OC[C@H](O)[C@@](O)(C)CO.C
InChI
1S/C5H13O7P/c1-5(8,3-6)4(7)2-12-13(9,10)11/h4,6-8H,2-3H2,1H3,(H2,9,10,11)/t4-,5+/m1/s1
InChI 密鑰
XMWHRVNVKDKBRG-UHNVWZDZSA-N
相关类别
應用
2-C-甲基-D-赤藓糖醇4-磷酸(MEP)是还原异构酶IspC的产物和第一个承诺的MEP途径中间体,用于研究类异戊二烯生物合成的非甲羟戊酸MEP途径。 MEP用作合成4-二磷酸胞苷-2-C-甲基d-赤藓糖醇(CDP-ME)的前体,CDP-ME是非甲羟戊酸途径的关键中间体。
生化/生理作用
一种对非甲羟戊酸MEP途径特异的代谢物中间体,通常在原核生物中发现,作为类异戊二烯以及非类异戊二烯(如维生素)的前体。由于该途径在人类中不存在,因此在寻找传染病的治疗方法中,其对开发细菌特异性药物是很有意义。
包裝
无底玻璃瓶。内含物装在插入的融合锥内。
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Sina I Odejinmi et al.
Tetrahedron, 68(43), 8937-8941 (2012-10-11)
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate (MEP) is a key chemical intermediate of the non-mevalonate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis employed by many pathogenic microbes. MEP is also the precursor for the synthesis of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl D-erythritol (CDP-ME), another key intermediate of the non-mevalonate pathway. As this
Hyungjin Eoh et al.
Tuberculosis (Edinburgh, Scotland), 89(1), 1-11 (2008-09-17)
Tuberculosis (TB) is still a major public health problem, compounded by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-TB co-infection and recent emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) and extensively drug resistant (XDR)-TB. Novel anti-TB drugs are urgently required. In this context, the 2C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate
Andréa Hemmerlin et al.
Progress in lipid research, 51(2), 95-148 (2011-12-27)
When compared to other organisms, plants are atypical with respect to isoprenoid biosynthesis: they utilize two distinct and separately compartmentalized pathways to build up isoprene units. The co-existence of these pathways in the cytosol and in plastids might permit the
J Kipchirchir Bitok et al.
ACS chemical biology, 7(10), 1702-1710 (2012-07-31)
There is significant progress toward understanding catalysis throughout the essential MEP pathway to isoprenoids in human pathogens; however, little is known about pathway regulation. The present study begins by testing the hypothesis that isoprenoid biosynthesis is regulated via feedback inhibition
Sinéad Heuston et al.
Microbiology (Reading, England), 158(Pt 6), 1389-1401 (2012-04-03)
Isoprenoid biosynthesis is essential for cell survival. Over 35 000 isoprenoid molecules have been identified to date in the three domains of life (bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes), and these molecules are involved in a wide variety of vital biological functions. Isoprenoids
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门