推荐产品
生物源
synthetic (chemical)
品質等級
化驗
89.0-100.5% anhydrous basis
形狀
powder
顏色
white to off-white
溶解度
H2O: 50 mg/mL
抗生素活性譜
Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-positive bacteria
作用方式
cell wall synthesis | interferes
儲存溫度
2-8°C
SMILES 字串
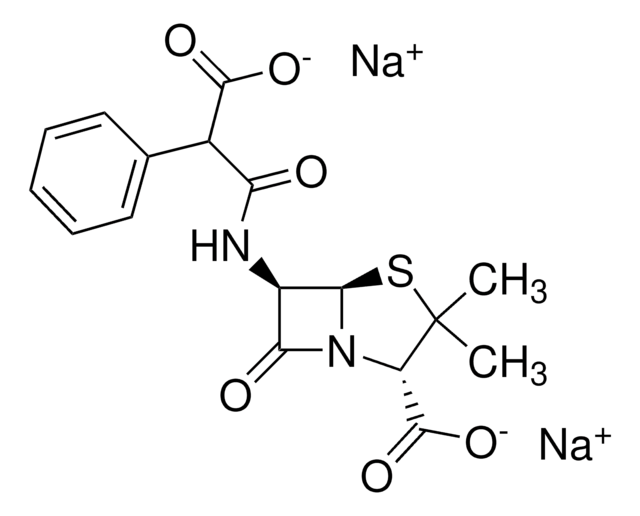
[Na+].[Na+].CC1(C)S[C@@H]2[C@H](NC(=O)C(C([O-])=O)c3ccccc3)C(=O)N2[C@H]1C([O-])=O
InChI
1S/C17H18N2O6S.2Na/c1-17(2)11(16(24)25)19-13(21)10(14(19)26-17)18-12(20)9(15(22)23)8-6-4-3-5-7-8;;/h3-7,9-11,14H,1-2H3,(H,18,20)(H,22,23)(H,24,25);;/q;2*+1/p-2/t9?,10-,11+,14-;;/m1../s1
InChI 密鑰
RTYJTGSCYUUYAL-YCAHSCEMSA-L
正在寻找类似产品? 访问 产品对比指南
一般說明
羧苄青霉素是一种半合成、广谱羧基青霉素抗生素,具有杀菌和抗β-内酰胺酶活性。它是一种广谱抗生素,即它能够有效对抗各种细菌,包括革兰氏阳性和革兰氏阴性细菌。羧苄青霉素对铜绿假单胞菌特别有效,铜绿假单胞菌是一种可以耐受其它抗生素的革兰氏阴性菌。
羧苄青霉素常用于细胞生物学应用,可防止细菌污染物的生长。在微生物学中,它也用于选择以含有编码β-内酰胺酶基因的载体转化的细菌,这使其耐受羧苄青霉素。
羧苄青霉素常用于细胞生物学应用,可防止细菌污染物的生长。在微生物学中,它也用于选择以含有编码β-内酰胺酶基因的载体转化的细菌,这使其耐受羧苄青霉素。
應用
羧苄青霉素二钠盐已用于:
- 制备LB琼脂平板和培养基
- 作为培养基中的选择剂用于防止细菌污染物的生长
- 开发单克隆抗体的研究
生化/生理作用
作用机制:羧青霉素抗生素,可通过灭活细菌细胞膜内表面的转肽酶来抑制细菌细胞壁合成(肽聚糖交联)。
抗微生物谱:具有抗革兰氏阳性和革兰氏阴性细菌活性。
抗微生物谱:具有抗革兰氏阳性和革兰氏阴性细菌活性。
羧苄青霉素通过打开内酰胺环,酰化青霉素敏感性转肽酶(penicillin-sensitive transpeptidase)的C-末端结构域。这种钝化作用防止了肽聚糖束(peptidoglycan strand)的交联,从而抑制了细菌细胞壁合成的第三和最后阶段。这导致细菌细胞壁的不完全合成,最终导致细胞溶解。
特點和優勢
- 具有杀菌和抗β-内酰胺酶活性的广谱抗生素
- 有效对抗各种细菌,包括铜绿假单胞菌
- 常用于细胞生物学和生物化学应用
- 提供优于氨苄青霉素的稳定性
儲存和穩定性
密闭。干燥。上锁保存或放置在只有经过授权或有资质的人员才能进入的区域。
分析報告
在 37°C 下可稳定保存 3 天
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 2
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
其他客户在看
Hae-Youn Lee et al.
Autophagy, 12(8), 1390-1403 (2016-06-24)
Autophagy, which is critical for the proper turnover of organelles such as endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria, affects diverse aspects of metabolism, and its dysregulation has been incriminated in various metabolic disorders. However, the role of autophagy of myeloid cells in
Tommaso Biancalani et al.
Molecular systems biology, 15(6), e8707-e8707 (2019-06-13)
Quantifying virulence remains a central problem in human health, pest control, disease ecology, and evolutionary biology. Bacterial virulence is typically quantified by the LT50 (i.e., the time taken to kill 50% of infected hosts); however, such an indicator cannot account
Nina Möker et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 192(7), 1946-1955 (2010-01-26)
Bacterial persister cells constitute a small portion of a culture which is tolerant to killing by lethal doses of bactericidal antibiotics. These phenotypic variants are formed in numerous bacterial species, including those with clinical relevance like the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas
John R Zupan et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(22), 9060-9065 (2013-05-16)
Growth and cell division in rod-shaped bacteria have been primarily studied in species that grow predominantly by peptidoglycan (PG) synthesis along the length of the cell. Rhizobiales species, however, predominantly grow by PG synthesis at a single pole. Here we
Sarah Sainsbury et al.
Journal of molecular biology, 405(1), 173-184 (2010-10-27)
We report the first crystal structures of a penicillin-binding protein (PBP), PBP3, from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in native form and covalently linked to two important β-lactam antibiotics, carbenicillin and ceftazidime. Overall, the structures of apo and acyl complexes are very similar;
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门