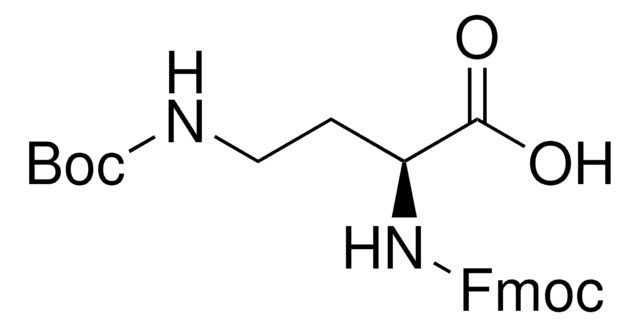
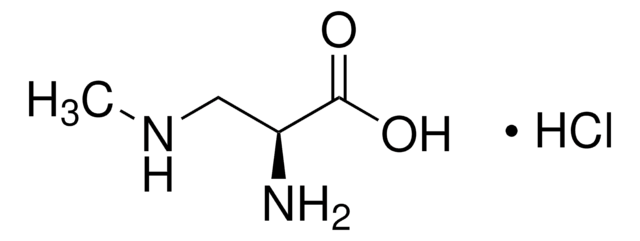
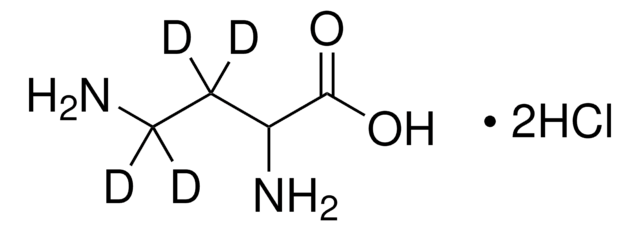
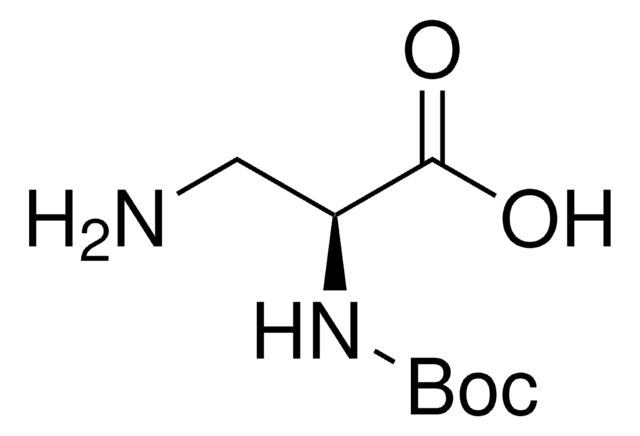
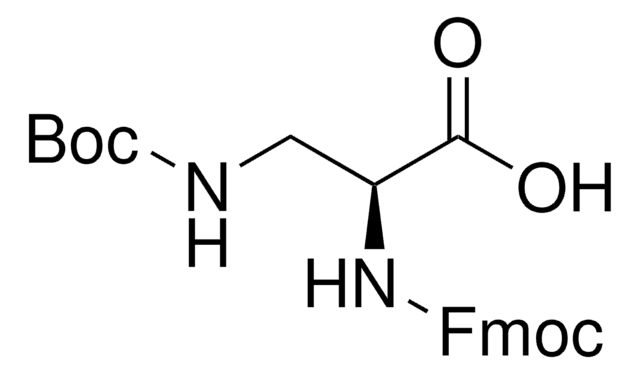
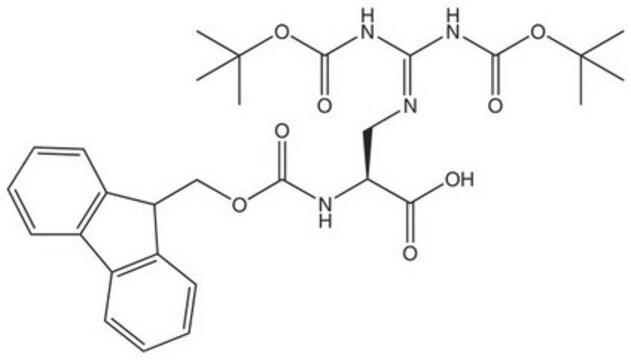
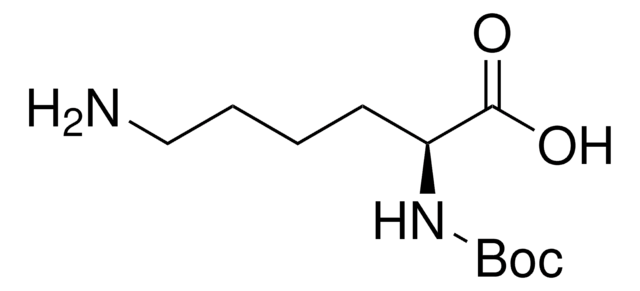
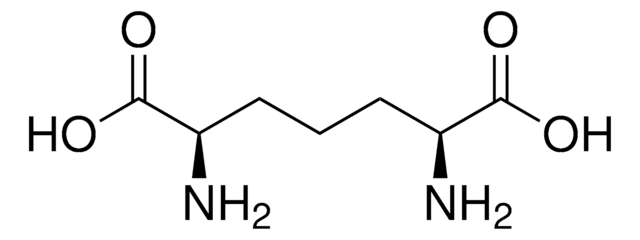
推荐产品
品質等級
化驗
≥95.0% (AT)
≥95.0%
光學活性
[α]20/D +14.5±1.5°, c = 3.67% in H2O
反應適用性
reaction type: solution phase peptide synthesis
mp
197-200 °C (dec.)
溶解度
water: soluble 0.5 g/10 mL
應用
peptide synthesis
SMILES 字串
Cl.Cl.NCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H10N2O2.2ClH/c5-2-1-3(6)4(7)8;;/h3H,1-2,5-6H2,(H,7,8);2*1H/t3-;;/m0../s1
InChI 密鑰
CKAAWCHIBBNLOJ-QTNFYWBSSA-N
正在寻找类似产品? 访问 产品对比指南
一般說明
L-2,4-二氨基丁酸二盐酸盐是非天然氨基酸衍生物。
應用
L-2,4-二氨基丁酸二盐酸盐可用于通过 HPLC-FD、UHPLC-UV、UHPLC-MS 和三重四极杆串联质谱法(UHPLC-MS/MS)从二氨基酸中区分出 β-N-甲基氨基-L-丙氨酸。它适用于定量海鲜中神经毒素 β-N-甲基氨基-L-丙氨酸(BMAA)。它可用作氨基酸分析的内标
注意
可能会释放出 HCl
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
標靶器官
Respiratory system
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Liying Jiang et al.
Scientific reports, 4, 6931-6931 (2014-11-07)
The neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) produced naturally by cyanobacteria, diatoms and dinoflagellates can be transferred and accumulated up the food chain, and may be a risk factor for neurodegenerative diseases. This study provides the first systematic screening of BMAA exposure of
Discovery of α,β- and α,γ-diamino acid scaffolds for the inhibition of M1 family aminopeptidases.
Rajesh Gumpena et al.
ChemMedChem, 6(11), 1971-1976 (2011-10-26)
Thomas Krüger et al.
Toxicon : official journal of the International Society on Toxinology, 55(2-3), 547-557 (2009-10-15)
Since diverse taxa of cyanobacteria has been linked to biosynthesis of BMAA, a controversy has arisen about the detection of neurotoxic amino acids in cyanobacteria. In this context, a novel LC-MS/MS method was developed for the unambiguous determination of beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine
Maria Hoernke et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1818(7), 1663-1672 (2012-03-22)
Basic amino acids play a key role in the binding of membrane associated proteins to negatively charged membranes. However, side chains of basic amino acids like lysine do not only provide a positive charge, but also a flexible hydrocarbon spacer
S A Banack et al.
Toxicon : official journal of the International Society on Toxinology, 56(6), 868-879 (2010-06-22)
The cyanobacterial neurotoxin beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) has been associated with certain forms of progressive neurodegenerative disease, including sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease. Reports of BMAA in cyanobacterial blooms from lakes, reservoirs, and other water resources continue to be made
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门