推荐产品
生物源
mouse
品質等級
抗體表格
purified antibody
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
Mobu-1, monoclonal
形狀
liquid
包含
≤0.1% sodium azide as preservative
物種活性(以同源性預測)
all
製造商/商標名
Calbiochem®
儲存條件
do not freeze
同型
IgG1
運輸包裝
wet ice
儲存溫度
2-8°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
一般說明
Anti-BrdU (Ab-3), mouse monoclonal, clone Mobu-1, recognizes BrdU. Requires biosynthetic labeling of the target cells with BrdU. It is validated for ICC and use with frozen and paraffin sections.
Purified mouse monoclonal antibody generated by immunizing mice with the specified immunogen and fusing splenocytes with P3-X63-Ag8-653 mouse myeloma cells (see application references). Recognizes BrdU (bromodeoxyuridine).
Recognizes BrdU (bromodeoxyuridine). Use of this antibody first requires biosynthetic labeling of the target cells with bromodeoxyuridine. This is the preferred BrdU antibody for staining.
免疫原
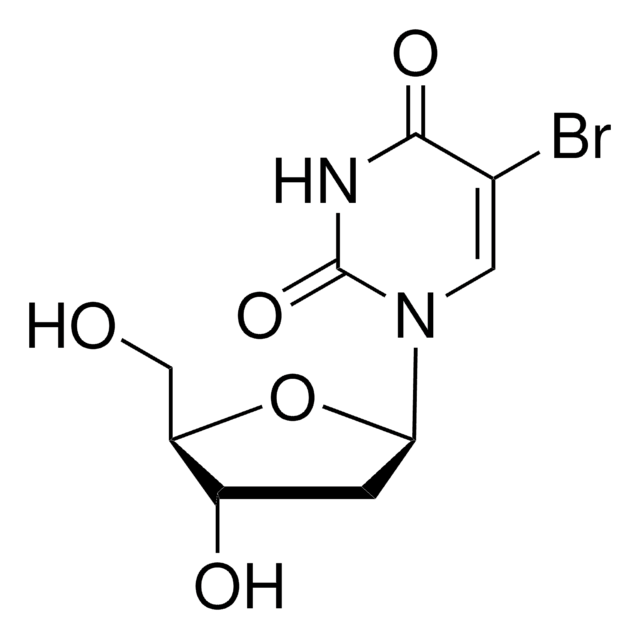
BrdU-labeled DNA
應用
Frozen Sections (2 g/ml)
Immunocytochemistry (1 g/ml)
Paraffin Sections (2.5 g/ml, trysin pre-treatment required)
Immunoblotting (not recommended)
包裝
Please refer to vial label for lot-specific concentration.
警告
Toxicity: Standard Handling (A)
外觀
In 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer, 0.2% gelatin, pH 7.5.
分析報告
Negative Control
Unlabeled cells
Unlabeled cells
Positive Control
BrdU labeled DNA
BrdU labeled DNA
其他說明
Gratzner, H.G. 1982. Science218, 474.
Gratzner, H.G. and Leif, R.C. 1981. Cytometry1, 385.
Gratzner, H.G. et al. 1975. Exp. Cell Res.95, 88.
Gratzner, H.G. and Leif, R.C. 1981. Cytometry1, 385.
Gratzner, H.G. et al. 1975. Exp. Cell Res.95, 88.
To enable antibody binding to the incorporated BrdU, cells must be fixed, permeabilized, and the DNA denatured. This is done in one step by treatment with Fixative/Denaturing Solution (70% EtOH, 0.1 N NaOH). Use of this antibody first requires biosynthetic labeling of the target cells with bromodeoxyuridine (Cat. No. 203806). Cultured cells can be pulse labeled with 10 µM bromodeoxyuridine for 30 minutes. For whole tissues, animals can be injected with 50 mg BrdU/kg body weight, sacrificed 1 h later, and the target organ(s) removed. Antibody should be titrated for optimal results in individual system.
法律資訊
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
其他客户在看
Ian B DeMeritt et al.
Virology, 346(1), 15-31 (2005-11-24)
Infection of fibroblasts by human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) rapidly activates the NF-kappaB signaling pathway, which we documented promotes efficient transactivation of the major immediate-early promoter (DeMeritt, I.B., Milford, L.E., Yurochko, A.D. (2004). Activation of the NF-kappaB pathway in human cytomegalovirus-infected cells
Shali Chen et al.
Molecular medicine reports, 22(1), 353-361 (2020-04-23)
20(S)‑Protopanaxadiol (PPD) is an active ginseng metabolite and is the final form of protopanaxadiol saponins metabolized by human intestinal microflora. The neuroprotective effects and mechanisms underlying PPD on neural stem cells (NSCs) are not completely understood. The aim of the
Patrick E Nyman et al.
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, 24(24), 6308-6318 (2018-08-09)
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), a common cancer worldwide, is etiologically associated with tobacco use, high alcohol consumption, and high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPV). The Notch signaling pathway, which is involved in cell differentiation decisions with differential downstream targets
F Aura Kullmann et al.
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology, 313(1), F85-F102 (2017-03-24)
The basal, intermediate, and superficial cell layers of the urothelium undergo rapid and complete recovery following acute injury; however, the effects of chronic injury on urothelial regeneration have not been well defined. To address this discrepancy, we employed a mouse
Sathish Kumar Mungamuri et al.
Cancer research, 66(9), 4715-4724 (2006-05-03)
Notch signaling is believed to promote cell survival in general. However, the mechanism is not clearly understood. Here, we show that cells expressing intracellular domain of human Notch1 (NIC-1) are chemoresistant in a wild-type p53-dependent manner. NIC-1 inhibited p53 by
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门