推荐产品
品質等級
化驗
≥98% (HPLC)
形狀
solid
製造商/商標名
Calbiochem®
儲存條件
OK to freeze
protect from light
顏色
pale yellow
溶解度
DMSO: 5 mg/mL
運輸包裝
ambient
儲存溫度
−20°C
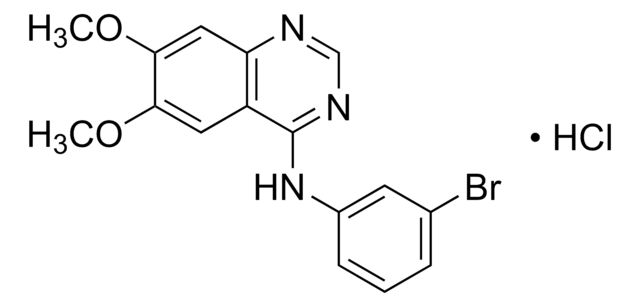
SMILES 字串
Clc1cc(ccc1)Nc2ncnc3c2cc(c(c3)OC)OC
InChI
1S/C16H14ClN3O2/c1-21-14-7-12-13(8-15(14)22-2)18-9-19-16(12)20-11-5-3-4-10(17)6-11/h3-9H,1-2H3,(H,18,19,20)
InChI 密鑰
GFNNBHLJANVSQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
一般說明
表皮生长因子受体激酶(IC50 = 3 nM)与HER2 neu(IC50 >100 µM)和血小板衍生生长因子受体激酶(IC50 >100 µM)相比,是一种细胞渗透性、可逆性、ATP竞争性、高效和选择性的抑制剂。消除血管紧张素II(目录号05-23-0101)诱导的MAP激酶(ERK)激活。还可抑制4-羟基壬烯醛对EGFR激酶和MAP激酶的激活。下调ARF1活性并分散高尔基体结构。也可购买10 mM(1 mg/317 µl)AG 1478的DMSO溶液(目录号658548)。
生化/生理作用
主要靶标
表皮生长因子受体激酶
表皮生长因子受体激酶
产物与ATP竞争。
可逆性:是
细胞可渗透性:是
靶标IC50:3 nM,针对表皮生长因子受体激酶
警告
毒性:标准处理(A)
準備報告
仅在使用前再用水相缓冲液进行稀释。
重構
复溶后,等分并冷冻保存(-20°C)。贮备溶液在-20°C下可稳定保存至多6个月。
其他說明
Pan, H., et al. 2008.J. Biol. Chem.283, In press.
Liu, W., et al. 1999.J. Cell Sci.112, 2409.
Eguchi, S., et al. 1998.J. Biol. Chem. 273, 8890.
Levitzki, A., and Gazit, A. 1995.Science267, 1782.
Fry, D.W., et al. 1994.Science265, 1093.
Osherov, N., and Levitski, A. 1994.Eur. J. Biochem.225, 1047.
Ward, W.H., et al. 1994.Biochem.Pharmacol.48, 659.
Liu, W., et al. 1999.J. Cell Sci.112, 2409.
Eguchi, S., et al. 1998.J. Biol. Chem. 273, 8890.
Levitzki, A., and Gazit, A. 1995.Science267, 1782.
Fry, D.W., et al. 1994.Science265, 1093.
Osherov, N., and Levitski, A. 1994.Eur. J. Biochem.225, 1047.
Ward, W.H., et al. 1994.Biochem.Pharmacol.48, 659.
法律資訊
根据美国专利号5,457,105和欧洲专利号0,566,266的许可证销售。
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
Sebastian Wurster et al.
Cell reports, 34(12), 108896-108896 (2021-03-25)
Severe and often fatal opportunistic fungal infections arise frequently following mucosal damage caused by trauma or cytotoxic chemotherapy. Interaction of fungal pathogens with epithelial cells that comprise mucosae is a key early event associated with invasion, and, therefore, enhancing epithelial
Zachary M Harris et al.
Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity, 2022, 9518592-9518592 (2022-10-05)
Studies have linked severe hyperoxia, or prolonged exposure to very high oxygen levels, with worse clinical outcomes. This study investigated the role of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in hyperoxia-induced lung injury at very high oxygen levels (>95%). Effects of
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门