推荐产品
品質等級
描述
Merck USA index - 14, 5269
化驗
≥95% (HPLC)
形狀
solid
製造商/商標名
Calbiochem®
儲存條件
OK to freeze
protect from light
顏色
orange
溶解度
DMSO: 10 mg/mL
ethanol: 10 mg/mL
運輸包裝
ambient
儲存溫度
2-8°C
SMILES 字串
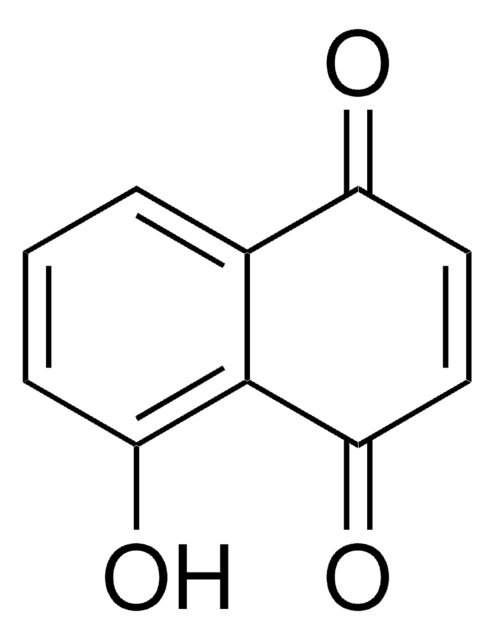
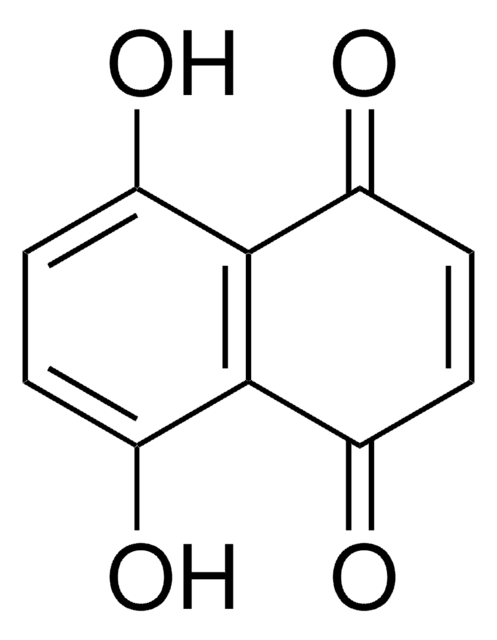
Oc1c2c(ccc1)C(=O)C=CC2=O
InChI
1S/C10H6O3/c11-7-4-5-9(13)10-6(7)2-1-3-8(10)12/h1-5,12H
InChI 密鑰
KQPYUDDGWXQXHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
一般說明
PPlases(细小蛋白家族的肽基-脯氨酰顺式/反式异构酶)的高选择性细胞渗透性,不可逆抑制剂。尚未报道其他已知的PPlase抑制剂(例如环孢菌素A,FK506和雷帕霉素)可抑制PPlases的细小蛋白家族。灭活显示是通过向胡桃酮中添加硫醇基团而不是通过任何氧化还原过程发生的。表现出抑菌和抑真菌作用。据报道对真核细胞具有细胞毒性,并通过RNA聚合酶II阻断转录。
胡桃酮最初是从核桃树的果壳和叶子中分离出来的,是肽基-脯氨酰顺/反异构酶(PPIase)的细小蛋白家族的高度选择性、细胞可渗透且不可逆的抑制剂。通过共价修饰目标酶中的巯基起作用。在真核细胞中表现出抑菌和抑真菌特性以及细胞毒性。还报道了通过核径流确定的RNA聚合酶I、II和III直接阻断真核细胞中的转录(IC50分别为7 µM,7 µM和2 µM)。通过修饰巯基破坏功能性预起始复合物的形成,但不会显著影响起始或延伸。不抑制限制性核酸内切酶或T7 RNA聚合酶。
生化/生理作用
主要靶标
PPIases(细小蛋白家族的肽基-脯氨酰顺式/反式异构酶)
PPIases(细小蛋白家族的肽基-脯氨酰顺式/反式异构酶)
产物不与ATP竞争。
可逆:否
细胞可渗透性:是
包裝
用惰性气体包装
警告
毒性:有毒(F)
重構
复溶后,等分并冷冻(-20°C)。储备溶液在-20°C下可稳定保存至多6个月。
其他說明
Chao, S.H., et al. 2001.Nucleic Acids Res.29, 767.
Hennig, L., et al. 1998.Biochemistry37, 5953.
Hennig, L., et al. 1998.Biochemistry37, 5953.
由于该运输中有害物质的性质,您的订单可能需要支付额外的运输费用。某些尺寸的产品可免除其他有害材料的运输费用。请与您当地的销售办事处联系,以获取有关这些费用的更多信息。
法律資訊
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Acute Tox. 3 Oral
儲存類別代碼
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
Insights and future directions of potential genetic therapy for Apert syndrome: A systematic review.
Nisreen Mohammed Al-Namnam et al.
Gene therapy, 28(10-11), 620-633 (2021-02-24)
Apert syndrome is a genetic disorder characterised by craniosynostosis and structural discrepancy of the craniofacial region as well as the hands and feet. This condition is closely linked with fibroblast growth factor receptor-2 (FGFR2) gene mutations. Gene therapies are progressively
Caixia Wu et al.
American journal of translational research, 13(10), 11162-11177 (2021-11-18)
Peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 is crucial for cell proliferation, but its role in pulmonary artery remodeling (PAR) is unclear. In the present study, we aimed to evaluate the expression and contribution of Pin1 in PAR. Treatment with Pin1 inhibitor Juglone or
Jia-Hua Hu et al.
Nature communications, 11(1), 1567-1567 (2020-03-29)
Voltage-gated K+ channels function in macromolecular complexes with accessory subunits to regulate brain function. Here, we describe a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 (Pin1)-dependent mechanism that regulates the association of the A-type K+ channel subunit Kv4.2 with its auxiliary subunit
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门