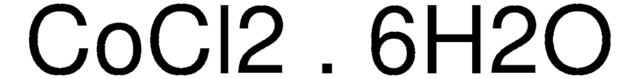推荐产品
蒸汽壓力
40 mmHg ( 0 °C)
品質等級
化驗
≥97%
97.0-102.0% (KT)
形狀
solid
負離子痕跡
nitrate (NO3-): ≤0.01%
sulfate (SO42-): ≤0.007%
正離子痕跡
Fe: ≤0.005%
Ni: ≤0.15%
Pb: ≤0.002%
Zn: ≤0.05%
SMILES 字串
O.O.O.O.O.O.Cl[Co]Cl
InChI
1S/2ClH.Co.6H2O/h2*1H;;6*1H2/q;;+2;;;;;;/p-2
InChI 密鑰
GFHNAMRJFCEERV-UHFFFAOYSA-L
正在寻找类似产品? 访问 产品对比指南
一般說明
Cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate, a hydrated form of cobalt chloride, is employed in electroplating and catalyst preparation. It serves as a precursor for synthesizing electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries and acts as a catalyst in a range of organic reactions, including acetylation, tosylation of alcohols, and condensation reactions.
應用
Cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate can be used as:
- An additive to the electron transport layer (ETL) in perovskite solar cells to improve their performance, particularly by reducing energy losses and increasing the open-circuit voltage.
- A cobalt source for doping ZnO nanostructures. The incorporation of cobalt ions into the ZnO matrix is crucial for modifying its electronic and optical properties.
- A precursor to modify cobalt metal-organic framework (Co-MOF) derived carbon microspheres for application as anode materials in lithium-ion batteries.
分析報告
不被硫化铵沉淀的物质(以硫酸盐形式)≤ 0.3 %
訊號詞
Danger
危險分類
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Carc. 1B Inhalation - Eye Dam. 1 - Muta. 2 - Repr. 1B - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
儲存類別代碼
6.1D - Non-combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic hazardous materials or hazardous materials causing chronic effects
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
其他客户在看
Electroplating and characterization of cobalt-nickel-iron and nickel-iron for magnetic microsystems applications
Rasmussen, FE., et al.
Sensors and actuators A, Physical, 92, 242-248 (2001)
Hyeohn Kim et al.
ACS nano, 15(1), 979-988 (2020-12-18)
Chiral inorganic nanomaterials have revealed opportunities in various fields owing to their strong light-matter interactions. In particular, chiral metal oxide nanomaterials that can control light and biochemical reactions have been highlighted due to their catalytic activity and biocompatibility. In this
Excellent lithium ion storage property of porous MnCo2O4 nanorods
Zeng, P., et al.
Royal Society of Chemistry Advances, 6, 23074-23084 (2016)
Sebastian Klemenz et al.
ChemSusChem, 11(18), 3150-3156 (2018-07-27)
High-performance catalysts for the oxygen-evolution reaction in water electrolysis are usually based on expensive and rare elements. Herein, mixed-metal borides are shown to be competitive with established electrocatalysts like noble metal oxides and other transition-metal(oxide)-based catalysts. Iron incorporation into nanoscale
One-step synthesis of cobalt and nitrogen co-doped carbon nanotubes and their catalytic activity for the oxygen reduction reaction
Fu, S., et al.
Journal of Material Chemistry A, 3, 12718-12722 (2015)
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门