L2637
Lipopolysaccharides from Escherichia coli O55:B5
purified by gel-filtration chromatography
Synonym(s):
LPS
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(4)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
Escherichia coli (O55:B5)
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
purified by
gel-filtration chromatography
impurities
<3% Protein
color
white to faint gray
solubility
water: soluble
shipped in
ambient
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
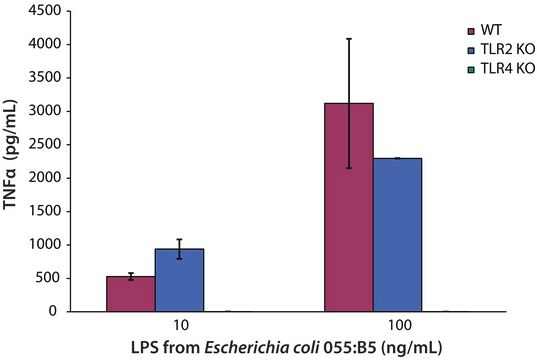
This product is extracted from E. coli serotype O55:B5 and purified by gel filtration. The source strain is CDC 1644-70. The LPS O55:B5 has been used to stimulate human peritoneal macrophages at 1 ng/ml and to stimulate equine peritoneal macrophages at 1-100 ng/ml.
Application
Lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) are characteristic components of the cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria. LPS and its lipid A moiety stimulate cells of the innate immune system by the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), a member of the Toll-like receptor protein family, which recognizes common pathogen-associated molecular-patterns (PAMPs).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are localized in the outer layer of the membrane and are, in noncapsulated strains, exposed on the cell surface. They contribute to the integrity of the outer membrane, and protect the cell against the action of bile salts and lipophilic antibiotics.
Preparation Note
The product is soluble in water (5 mg/ml) or cell culture medium (1 mg/ml) yielding a hazy, faint yellow solution. A more concentrated, though still hazy, solution (20 mg/ml) has been achieved in aqueous saline after vortexing and warming to 70-80 oC. Lipopolysaccharides are molecules that form micelles in every solvent. Hazy solutions are observed in water and phosphate buffered saline. Organic solvents do not give clearer solutions. Methanol yields a turbid suspension with floaters, while water yields a homogeneously hazy solution.
Other Notes
To gain a comprehensive understanding of our extensive range of Lipopolysaccharides for your research, we encourage you to visit our Carbohydrates Category page.
related product
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 2 Oral
Storage Class Code
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
J Vier et al.
Cell death & disease, 7, e2103-e2103 (2016-02-20)
Neutrophil granulocytes are innate effector cells of the first line of defense against pyogenic bacteria. Neutrophil lifespan is short, is prolonged by pro-inflammatory stimuli, controls functionality of the cells and can determine tissue damage. Experimental analysis of primary neutrophils is
Yunru Ren et al.
Water research, 154, 153-161 (2019-02-21)
Aerosolized reclaimed water can cause inflammatory responses in lung after inhalation, and endotoxin has been identified as the main inducer. Since the effects of disinfection treatments on endotoxins had conflicting results, this study explored the changes of endotoxin activity and
John Bienenstock et al.
PloS one, 8(10), e76236-e76236 (2013-10-08)
Human milk oligosaccharides (HMO) are being studied by different groups exploring a broad range of potential beneficial effects to the breastfed infant. Many of these effects have been attributed to a growth promotion effect on certain gut organisms such as
Francisco J Quintana et al.
PloS one, 3(10), e3509-e3509 (2008-10-24)
B-cells integrate antigen-specific signals transduced via the B-cell receptor (BCR) and antigen non-specific co-stimulatory signals provided by cytokines and CD40 ligation in order to produce IgG antibodies. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) also provide co-stimulation, but the requirement for TLRs to generate
Xiangdong Lu et al.
Cell reports, 28(2), 472-485 (2019-07-11)
The NuRD complex contains both chromatin remodeling and histone deacetylase activities. Mice lacking the MTA2 subunit of NuRD show developmental defects in pro-B, pre-B, immature B, and marginal zone B cells, and abnormal germinal center B cell differentiation during immune
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service