A0157
Ascorbate Oxidase from Cucurbita sp.
lyophilized powder, 1,000-3,000 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
L-Ascorbate:oxygen oxidoreductase, Ascorbase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
plant (Cucurbita spp.)
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
1,000-3,000 units/mg protein
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Ascorbate oxidase is a homodimeric enzyme, which comprises 552 amino acid residues per subunit (zucchini). It corresponds to a molecular mass of 70kDa per subunit. This enzyme is mainly found in plants, fungi and eubacteria.
Application
Ascorbate Oxidase from Cucurbita sp. has been used:
- as a supplement in the culture medium for differentiation into osteoblasts
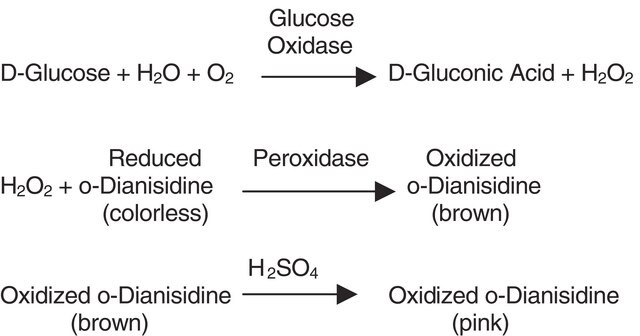
- to oxidize ascorbic acid producing monodehydroascorbate in monodehydroascorbate reductase assay
- in determining ascorbate (AsA) and dehydroascorbate (DHA) concentrations
Ascorbate oxidase, from Cucurbita sp., may be used to study oxidative stress and heat stress response and tolerance. Ascorbate oxidase, from Sigma, has been used in ascorbic acid assays to study the heat stress response of Arabidopsis .
Biochem/physiol Actions
Ascorbate oxidase (AO) participates in cell growth by regulating reduction/oxidation (redox) of the apoplast. This enzyme can synthesize the oxidative molecule dehydroascorbate acid (DHA) in the apoplast. It is also involved in cell elongation and enlargement development.
Ascorbate oxidase converts ascorbic acid to dehydroascorbic acid. It is highly specific for L-ascorbic acid and a few analogs. Ascorbate oxidase exists as a dimer and has a molecular weight of approximately 140 kDa.
Unit Definition
One unit will oxidize 1.0 μmole of L-ascorbate to dehydroascorbate per min at pH 5.6 at 25 °C.
Physical form
Lyophilized powder containing buffers and sucrose as stabilizer.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Sudhakar Srivastava et al.
Protoplasma, 248(4), 805-815 (2010-12-29)
Arsenic (As) is a potential hazard to plants' health, however the mechanisms of its toxicity are yet to be properly understood. To determine the impact of redox state and energetic in stress imposition, plants of Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle, which
Kyoko Fujita et al.
Biopolymers, 93(12), 1093-1099 (2010-07-29)
Hydrated choline dihydrogen phosphate (Hy[ch][dhp]) containing 30 wt% water was investigated as a novel protein solvent. The Hy[ch][dhp] dissolved some metallo proteins (cytochrome c, peroxidase, ascorbate oxidase, azurin, pseudoazurin and fructose dehydrogenase) without any modification. These proteins retained the surroundings
Ann Wambui Munyaka et al.
Journal of food science, 75(4), C336-C340 (2010-06-16)
The thermal stability of vitamin C (including l-ascorbic acid [l-AA] and dehydroascorbic acid [DHAA]) in crushed broccoli was evaluated in the temperature range of 30 to 90 degrees C whereas that of ascorbic acid oxidase (AAO) was evaluated in the
Michael Wawire et al.
Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 59(5), 1774-1783 (2011-02-12)
Cowpea, an African leafy vegetable ( Vigna unguiculata ), contains a high level of vitamin C. The leaves harvested at 4-9 weeks are highly prone to vitamin C losses during handling and processing. Therefore, the purpose of this research was
Nidhi Chauhan et al.
The Analyst, 136(9), 1938-1945 (2011-03-19)
An ascorbate oxidase (AsOx) (E.C.1.10.3.3) purified from Lagenaria siceraria fruit was immobilized covalently onto a carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes and polyaniline (c-MWCNT/PANI) layer electrochemically deposited on the surface of an Au electrode. The diffusion coefficient of ascorbic acid was determined
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service