93750
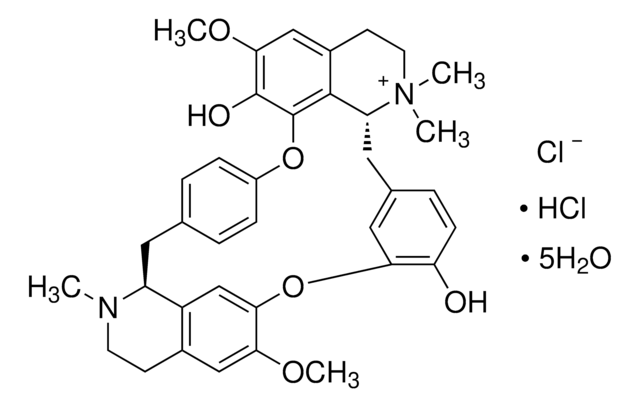
(+)-Tubocurarine chloride pentahydrate
≥97.0% (TLC)
Synonym(s):
(+)-Tubocurarine chloride hydrochloride pentahydrate, D-Tubocurarine dichloride pentahydrate, Tubarine pentahydrate
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
plant
Quality Level
Assay
≥97.0% (TLC)
form
powder
optical activity
[α]20/D +195±5°, c = 0.5% in H2O
impurities
~12% water
mp
275-280 °C (dec.) (lit.)
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
[Cl-].Cl[H].[H]O[H].[H]O[H].[H]O[H].[H]O[H].[H]O[H].COc1cc2CCN(C)[C@H]3Cc4ccc(Oc5c(O)c(OC)cc6CC[N+](C)(C)[C@H](Cc7ccc(O)c(Oc1cc23)c7)c56)cc4
InChI
1S/C37H40N2O6.2ClH.5H2O/c1-38-14-12-24-19-32(42-4)33-21-27(24)28(38)16-22-6-9-26(10-7-22)44-37-35-25(20-34(43-5)36(37)41)13-15-39(2,3)29(35)17-23-8-11-30(40)31(18-23)45-33;;;;;;;/h6-11,18-21,28-29H,12-17H2,1-5H3,(H-,40,41);2*1H;5*1H2/t28-,29+;;;;;;;/m0......./s1
InChI key
WMIZITXEJNQAQK-GGDSLZADSA-N
Gene Information
human ... CHRNA1(1134) , CHRNB1(1140) , CHRND(1144) , CHRNE(1145) , CHRNG(1146)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
- as an acetylcholine receptor antagonist in synapse blocking experiment to study its effect on neuromuscular junction formation (NMJ) formation in a co-culture system of human skeletal muscles and human stem cell-derived motoneurons
- to induce paralysis in zebrafish larvae to study whole-brain imaging of seizures by two-photon light-sheet microscopy
- to block NMJ to study its role in myotube contraction
Biochem/physiol Actions
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Oral
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service