570303
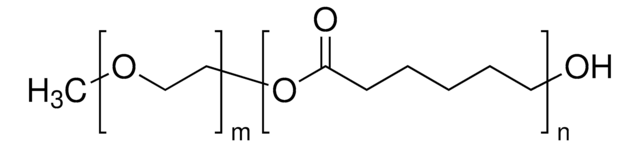
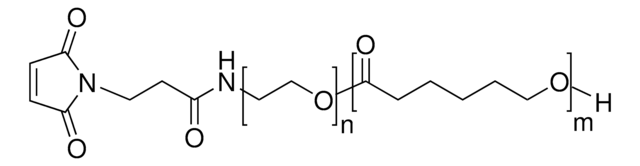
Poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(ε−caprolactone) methyl ether
PEG average Mn ~5,000, PCL average Mn ~5,000
Synonym(s):
Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether-block-poly(ε−caprolactone)
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
solid
Quality Level
mol wt
PCL average Mn ~5,000
PEG average Mn ~5,000
average Mn ~10,000 (total)
degradation timeframe
>12 months
mp
52.8-56.1 °C
54.2-55.9 °C (lit.)
Mw/Mn
<1.4
PDI
<1.4
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Features and Benefits
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Microparticle drug delivery systems have been extensively researched and applied to a wide variety of pharmaceutical and medical applications due to a number of advantages including injectability, local applicability to target tissues and sites, and controlled drug delivery over a given time period.
Professor Nicola Tirelli (Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia, Italy) highlights the microfluidic-assisted method for fabricating well-defined and reproducible nanoparticles for drug delivery research.
Professor Nicola Tirelli (Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia, Italy) highlights the microfluidic-assisted method for fabricating well-defined and reproducible nanoparticles for drug delivery research.
The development of drugs that target specific locations within the human body remains one of the greatest challenges in biomedicine today.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service