457876
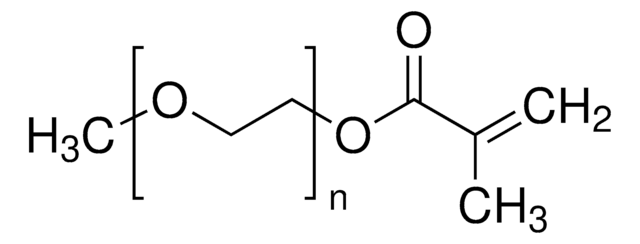
Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate solution
average Mn 2,000, 50 wt. % in H2O
Synonym(s):
Polyethylene glycol
About This Item
Recommended Products
mol wt
average Mn 2,000
Quality Level
reaction suitability
reagent type: chemical modification reagent
reaction type: Polymerization Reactions
concentration
50 wt. % in H2O
refractive index
n20/D 1.4054
density
1.079 g/mL at 25 °C
Ω-end
methacrylate
α-end
methoxy
polymer architecture
shape: linear
functionality: monofunctional
SMILES string
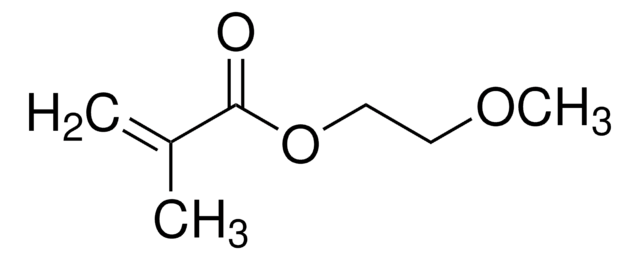
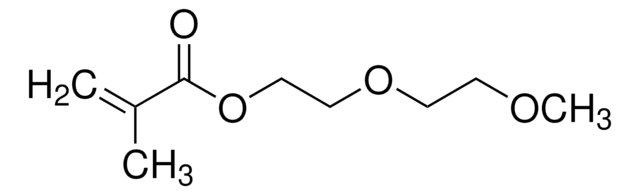
COCCOCCOCCOCCOC(=O)C(C)=C
Related Categories
General description
Application
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Devising biomaterial scaffolds that are capable of recapitulating critical aspects of the complex extracellular nature of living tissues in a threedimensional (3D) fashion is a challenging requirement in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service