All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
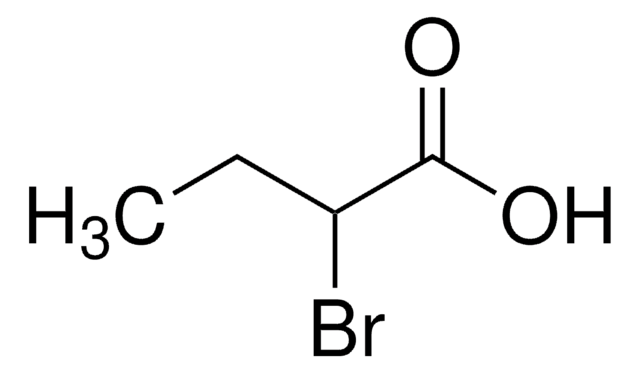
CH2BrCHBrCOOH
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
231.87
Beilstein:
1721428
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
98%
form
solid
bp
160 °C/20 mmHg (lit.)
mp
64-66 °C (lit.)
functional group
bromo
carboxylic acid
SMILES string
OC(=O)C(Br)CBr
InChI
1S/C3H4Br2O2/c4-1-2(5)3(6)7/h2H,1H2,(H,6,7)
InChI key
ZMYAKSMZTVWUJB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
2,3-Dibromopropionic acid was used in chemical shift imaging during analysis of multiple samples by multiplex sample NMR methodology. It was used as surrogate standard during extraction and determination of haloacetic acid in drinking water.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class Code
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Carles Planas et al.
Analytical and bioanalytical chemistry, 411(17), 3905-3917 (2019-06-04)
A fast, simple, selective, and sensitive method for the analysis of 11 haloacetic acids (HAAs) in chlorine-treated water has been developed. The method is based on liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry (LC/ESI-QqQ-MS/MS) with direct injection of the aqueous
Occurrence and Determination of Haloacetic Acids in Metro Manila Drinking Water.
Rodriguez IB and Espino MPB.
Science Diliman, 21(2), 35-41 (2010)
T Hou et al.
Analytical chemistry, 73(11), 2541-2546 (2001-06-14)
Two improved approaches for the rapid analysis of multiple samples using multiplex sample NMR are described. In the first approach, frequency-selective 90 degrees radio frequency pulses and large pulsed field gradients are applied to excite and detect multiple samples in
Tarek Manasfi et al.
International journal of hygiene and environmental health, 220(3), 583-590 (2017-02-16)
An undesirable consequence of disinfection is the formation of chemical contaminants known as disinfection byproducts (DBPs). Chronic exposure to DBPs has been linked to adverse health effects. The occurrence of DBPs in chlorinated pools filled with seawater (such as thalassotherapy
Tarek Manasfi et al.
International journal of hygiene and environmental health, 222(1), 1-8 (2018-07-23)
Chlorination of seawater is one of the most effective technologies for industrial biofouling control. However, chlorination leads to the formation of halogenated chlorination byproducts (CBPs) associated with potential risks to environmental and human health. The present study investigated the occurrence
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service