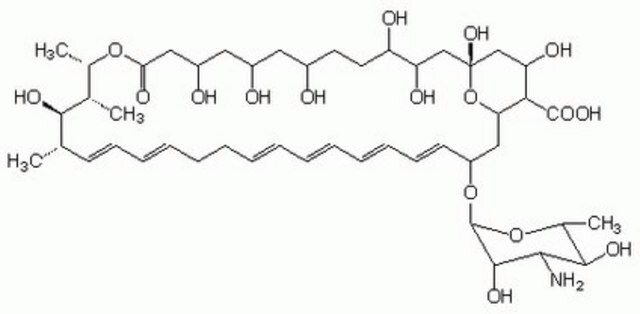
SRP8051
CD152 (human): FC (human) (non-lytic)
recombinant, expressed in CHO cells, ≥98% (SDS-PAGE)
Synonym(s):
CTLA-4, Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4, Hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 2
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
human
recombinant
expressed in CHO cells
Assay
≥98% (SDS-PAGE)
form
lyophilized
mol wt
monomer 39 kDa by calculation
packaging
pkg of 100 μg
impurities
<0.06 EU/μg endotoxin, tested
color
white
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
human ... CTLA4(1493)
General description
CD152 and CD28 are both expressed on the cell surface as homodimers or as monomers. CD152 was originally identified as a gene that was specifically expressed by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. However, CD152 transcripts have since been found in both Th1 and Th2, and CD4+ and CD8+ T cell clones. Whereas, CD28 expression is constitutive on the surfaces of 95% of CD4+ T cells and 50% of CD8+ T cells and is down regulated upon T cell activation, CD152 expression is upregulated rapidly following T cell activation and peaks approximately 24 hours following activation. Although both CD152 and CD28 can bind to the same ligands, CD152 binds to B71 and B72 with 20-100-fold higher affinity than CD28.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Physical form
Reconstitution
Other Notes
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service