S4503
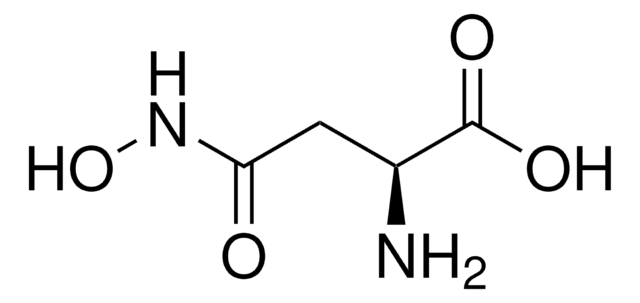
DL-Serine hydroxamate
≥97% (TLC), suitable for ligand binding assays
Synonym(s):
SHX
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C3H8N2O3
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
120.11
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352209
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.26
Recommended Products
product name
DL-Serine hydroxamate, seryl-tRNA synthetase inhibitor
Assay
≥97% (TLC)
form
powder
technique(s)
ligand binding assay: suitable
color
white to off-white
application(s)
cell analysis
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
NC(CO)C(=O)NO
InChI
1S/C3H8N2O3/c4-2(1-6)3(7)5-8/h2,6,8H,1,4H2,(H,5,7)
InChI key
LELJBJGDDGUFRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
Application
Serine has been used as an inhibitor of seryl-tRNA synthetase. DL-Serine hydroxamate is used to induce metabolic synthesis of guanosine 3′-diphosphate 5′-diphosphate (ppGpp) in E. coli by amino acid starvation. It is also used to synchronize cell cycle in E. coli cultures by inhibition of tRNA charging.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Serine is involved in the one-carbon unit metabolism. It is associated with the biosynthesis of cysteine, ceramide, phosphatidylserine, purine and pyrimidine. In bacteria, it participates in tryptophan synthesis. Gluconeogenesis, one of the important biochemical processes, involves serine, particularly in ruminants. Protein phosphorylation is one such event that utilizes serine. Glycine, a metabolic product of serine, serves as an antioxidant and a neurotransmitter. D-serine is known to activate the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors of the brain. Serine hydroxamate, a structural analogue of serine prevents seryl-tRNA (transfer ribonucleic acid) charging and thereby decreases phospholipid and nucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Olaf Brockmann-Gretza et al.
BMC genomics, 7, 230-230 (2006-09-12)
The stringent response is the initial reaction of microorganisms to nutritional stress. During stringent response the small nucleotides (p)ppGpp act as global regulators and reprogram bacterial transcription. In this work, the genetic network controlled by the stringent response was characterized
Dao Nguyen et al.
Science (New York, N.Y.), 334(6058), 982-986 (2011-11-19)
Bacteria become highly tolerant to antibiotics when nutrients are limited. The inactivity of antibiotic targets caused by starvation-induced growth arrest is thought to be a key mechanism producing tolerance. Here we show that the antibiotic tolerance of nutrient-limited and biofilm
H J Cha et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 65(2), 409-414 (1999-01-30)
We constructed and characterized three stress probe plasmids which utilize a green fluorescent protein as a noninvasive reporter in order to elucidate Escherichia coli cellular stress responses in quiescent or resting cells. Cellular stress levels were easily detected by fusing
Yuki Matsumoto et al.
BMC genomics, 14, 808-808 (2013-11-21)
Cell growth rate reflects an organism's physiological state and largely relies on the ability of gene expression to respond to the environment. The relationship between cellular growth rate and gene expression remains unknown. Growth rate-coordinated changes in gene expression were
B Belitsky et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 257(9), 4677-4679 (1982-05-10)
Lack of three different amino acids or treatment with the analogue DL-serine hydroxamate does not induce the accumulation of ppGpp and pppGpp, the 3'-pyrophosphates of GDP and GTP, respectively, in Rhizobium meliloti strain 41. Surprisingly, RNA accumulation is controlled under
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service