MAK290
Trypsin Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit
sufficient for 100 colorimetric tests
Synonym(s):
Trypsin Enzyme Activity Kit
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12161503
NACRES:
NA.84
Recommended Products
detection method
colorimetric
relevant disease(s)
gastrointestinal diseases
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
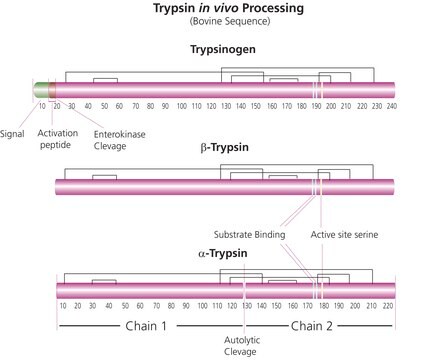
Trypsin (EC 3.4.21.4) is a pancreatic serine protease, which hydrolyzes peptide bonds specifically at the carboxyl side of arginine and lysine residues. The rate of hydrolysis is slower if an acidic residue is on either side of the cleavage site and cleavage may not occur if a proline residue is on the carboxyl side. Tryptic digestion of the protein of interest results in a highly specific cleavage and a limited number of peptide fragments.
Suitability
Suitable for the detection of Trypsin activity in various samples.
Principle
In this assay, trypsin cleaves a substrate to generate p-nitroaniline (p-NA) which is detected at λ= 405 nm. Since the color intensity is proportional to p-NA content, trypsin activity can be accurately measured. The kit detects 10–100 mU (p-NA unit) trypsin in various samples.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1 - Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
A Aderibigbe et al.
Poultry science, 99(10), 5007-5017 (2020-09-30)
Trypsin inhibitors (TI) resident in soybeans affects protein utilization. While heat treatment influences residual TI, it simultaneously affects the structure and solubility of the soybean proteins and confounds any response to exogenous proteases. Using purified TI, the effect of exogenous
Ahmad Farooq et al.
Gastroenterology, 161(3), 982-995 (2021-05-30)
Heavy alcohol consumption is a common cause of acute pancreatitis; however, alcohol abuse does not always result in clinical pancreatitis. As a consequence, the factors responsible for alcohol-induced pancreatitis are not well understood. In experimental animals, it has been difficult
Ali Hanafiah Hakim et al.
Animals : an open access journal from MDPI, 12(7) (2022-04-13)
The study aimed at determining the ileal nutrient digestibility, digestive enzyme activity, intestinal morphology, and nutrient transporters mRNA expressions in broiler chickens fed with fermented PKC (LPKC) based diets with different levels of fat supplementation under hot and humid conditions.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service