SAB4200855
Anti-Cytokeratin Peptide 18 antibody, Mouse monoclonal
clone CY-90, purified from hybridoma cell culture
Synonym(s):
Anti-CK18
About This Item
Recommended Products
antibody form
purified from hybridoma cell culture
Quality Level
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
CY-90, monoclonal
form
liquid
species reactivity
human
concentration
~1 mg/mL
technique(s)
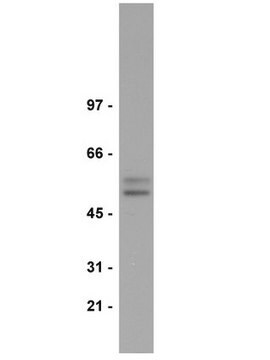
immunoblotting: suitable
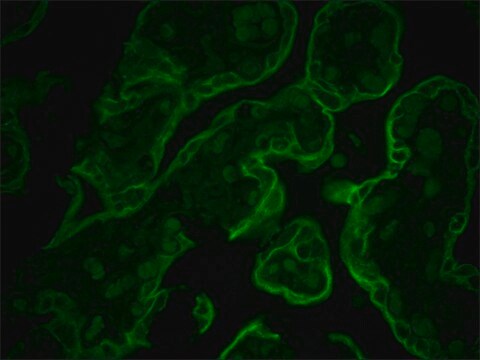
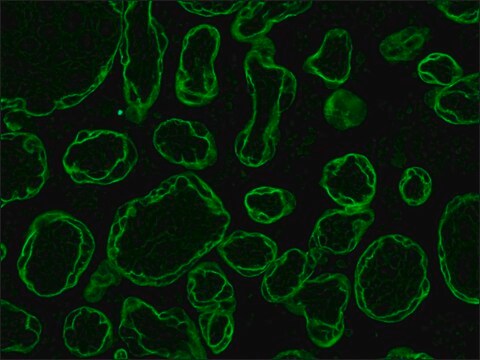
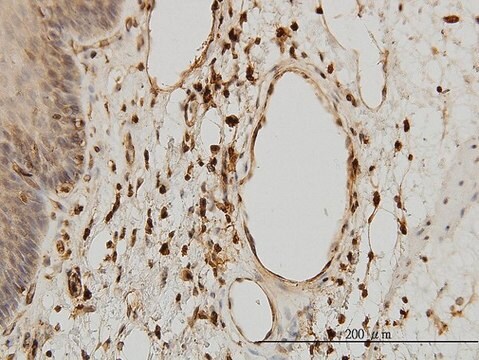
immunohistochemistry: 10-20 μg/mL using heat-retrieved formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human placenta sections
isotype
IgG1
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
General description
Specificity
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cytokeratin 18 is a member of the type I subfamily. Cytokeratin pair 8/18 forms the IF scaffold predominantly in simple epithelia such as the liver and pancreas. They have major role in the mechanical support of the cell, protein biosynthesis, protection from apoptosis, regulation of cell cycle progression, motility and organelle transport.3
Cytokeratins over and misexpression are linked to various diseases and more than 60 different disorders (termed as keratinopathies) have been linked to inherited cytokeratin changes. Cytokeratins (such as cytokeratin 18) serve as serum markers for malignant and non-neoplastic disorders and mutation of human cytokeratin 18 has also been associated with liver diseases.7
Physical form
Storage and Stability
Disclaimer
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service