E8283
pFLAG-CTS™ Expression Vector
Bacterial vector for periplasmic expression of C-terminal FLAG fusion proteins
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
Recommended Products
tag
FLAG® tagged
grade
for molecular biology
form
buffered aqueous solution
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
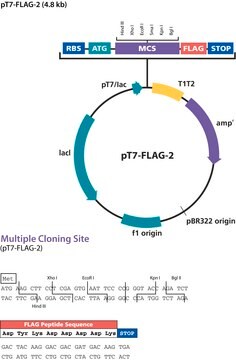
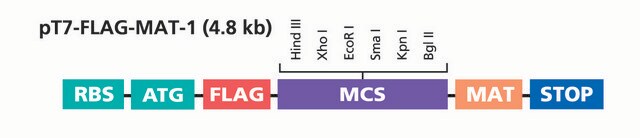
The pFLAG-CTS™ Expression Vector is a 5.3 kb E. coli expression vector used for cytoplasmic expression of a properly inserted open reading frame as a C-terminal FLAG® fusion protein. The FLAG epitope is a small, hydrophilic 8 amino acid tag (DYKDDDDK) that provides for sensitive detection and high quality purification using ANTI-FLAG products.
C-terminal FLAG fusion proteins may be purified using Monoclonal ANTI-FLAG M2, Catalog Number F3165, and ANTI-FLAG M2 Affinity Gel, Catalog Number A2220.
The pFLAG-CTS-BAP Control Plasmid is a 6.7 kb E. coli plasmid used for efficient and controlled periplasmic expression of C-terminal FLAG-BAP fusion protein.
Vector Maps and Sequences
C-terminal FLAG fusion proteins may be purified using Monoclonal ANTI-FLAG M2, Catalog Number F3165, and ANTI-FLAG M2 Affinity Gel, Catalog Number A2220.
The pFLAG-CTS-BAP Control Plasmid is a 6.7 kb E. coli plasmid used for efficient and controlled periplasmic expression of C-terminal FLAG-BAP fusion protein.
Vector Maps and Sequences
Application
The pFLAG-CTS™ Expression Vector is suitable for cloning and expression of C-terminal FLAG® fusion proteins in E. coli.
Components
- pFLAG-CTS™ Expression Vector 10 μg (E5269) is supplied as 0.5 mg/ml in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) with 1 mM EDTA.
- pFLAG-CTS™-BAP Control Plasmid 1 μg (P7707) is supplied as 0.5 mg/ml in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) with 1 mM EDTA.
Principle
The promoter-regulatory region of the strong tac promoter (a hybrid of the trp and lac promoters from E.coli) drives transcription of ORF-FLAG fusion constructs. Control of transcription is regulated by the presence of the lacO sequences and inclusion of the lac repressor gene (lacI) on the plasmid.
Legal Information
FLAG is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
pFLAG-CTS is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
H A de Boer et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 80(1), 21-25 (1983-01-01)
Two hybrid promoters that are functional in Escherichia coli have been constructed. These hybrid promoters, tacI and tacII, were derived from sequences of the trp and the lac UV5 promoters. In the first hybrid promoter (tacI), the DNA upstream of
Jianzhi Zhang
Nature genetics, 38(7), 819-823 (2006-06-13)
Similar morphological or physiological changes occurring in multiple evolutionary lineages are not uncommon. Such parallel changes are believed to be adaptive, because a complex character is unlikely to originate more than once by chance. However, the occurrence of adaptive parallel
Chomphunuch Songsiriritthigul et al.
Microbial cell factories, 9, 20-20 (2010-04-13)
Mannans are one of the key polymers in hemicellulose, a major component of lignocellulose. The Mannan endo-1,4-beta-mannosidase or 1,4-beta-D-mannanase (EC 3.2.1.78), commonly named beta-mannanase, is an enzyme that can catalyze random hydrolysis of beta-1,4-mannosidic linkages in the main chain of
Saadet Albayrak Guralp et al.
PloS one, 8(3), e59305-e59305 (2013-03-26)
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) belong to a class of natural microbicidal molecules that have been receiving great attention for their lower propensity for inducing drug resistance, hence, their potential as alternative drugs to conventional antibiotics. By generating AMP libraries, one can
Hao Yu et al.
Microbiology (Reading, England), 158(Pt 3), 612-621 (2011-12-17)
Cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 (CNF1), a Rho GTPase-activating bacterial toxin, has been shown to contribute to invasion by meningitis-causing Escherichia coli K1 of human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMEC), which constitute the blood-brain barrier. However, CNF1 is a cytosolic protein
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service