C2240
Anti-Calcium Channel CaV3.1 (α1G) antibody produced in rabbit
affinity isolated antibody, lyophilized powder
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
affinity isolated antibody
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
lyophilized powder
species reactivity
rat
technique(s)
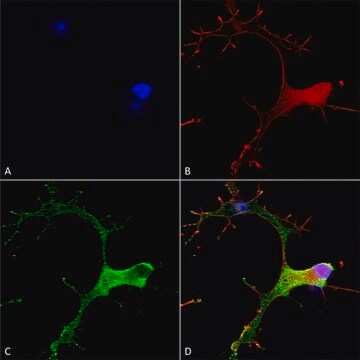
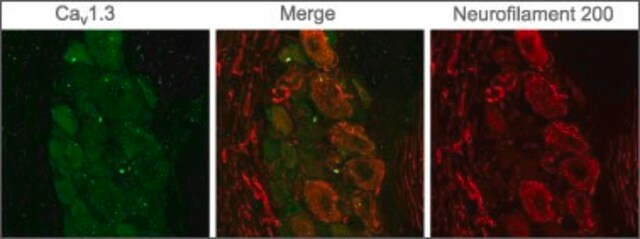
western blot: 1:200 using rat brain membranes
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... CACNA1G(8913)
rat ... Cacna1g(29717)
Related Categories
General description
Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, T type, α 1G subunit is a protein encoded by CACNA1G gene in humans. It belongs to a family of voltage-gated calcium channels and serves as the key transducer of cell surface membrane potential changes into local intracellular calcium transients that initiate many different physiological events.
Immunogen
peptide corresponding to amino acid residues 1-22 of rat CaV3.1. This epitope is highly homologous in human (20/22 residues identical).
Application
Anti-Calcium Channel CaV3.1 (α1G) antibody produced in rabbit is suitable for western blotting at a dilution of 1:200 using rat brain membranes.
Biochem/physiol Actions
CACNA1G (T-type channels) are involved in pacemaker activity, low-threshold calcium spikes, neuronal oscillations and resonance and rebound burst firing. It exhibits a significant window current that helps for Fe2+ pathway entry into cells with relevant concentrations of extracellular Fe2+. The window current also creates a pathway for Cd2+ entry into cells during Cd2+ exposure. CACNA1G were found to be associated with Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Physical form
Lyophilized from phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 1% bovine serum albumin, and 0.05% sodium azide.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
E Perez-Reyes et al.
Nature, 391(6670), 896-900 (1998-03-12)
The molecular diversity of voltage-activated calcium channels was established by studies showing that channels could be distinguished by their voltage-dependence, deactivation and single-channel conductance. Low-voltage-activated channels are called 'T' type because their currents are both transient (owing to fast inactivation)
S P Strom et al.
Molecular psychiatry, 15(10), 996-1005 (2009-05-21)
Chromosome 17q11-q21 is a region of the genome likely to harbor susceptibility to autism (MIM(209850)) based on earlier evidence of linkage to the disorder. This linkage is specific to multiplex pedigrees containing only male probands (MO) within the Autism Genetic
Kyle V Lopin et al.
Molecular pharmacology, 82(6), 1194-1204 (2012-09-14)
Iron is a biologically essential metal, but excess iron can cause damage to the cardiovascular and nervous systems. We examined the effects of extracellular Fe²⁺ on permeation and gating of Ca(V)3.1 channels stably transfected in HEK293 cells, by using whole-cell
William A Catterall et al.
Pharmacological reviews, 57(4), 411-425 (2005-12-31)
The family of voltage-gated calcium channels serves as the key transducers of cell surface membrane potential changes into local intracellular calcium transients that initiate many different physiological events. There are 10 members of the voltage-gated calcium channel family that have
Kyle V Lopin et al.
Molecular pharmacology, 82(6), 1183-1193 (2012-09-14)
Cd²⁺ is an industrial pollutant that can cause cytotoxicity in multiple organs. We examined the effects of extracellular Cd²⁺ on permeation and gating of Ca(v)3.1 (α1G) channels stably transfected in HEK293 cells, by using whole-cell recording. With the use of
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service