S7160
ApopTag Fluorescein Direct In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit
About This Item
Recommended Products
technique(s)
flow cytometry: suitable
immunocytochemistry: suitable
Quality Level
detection method
fluorometric
General description
Of all the aspects of apoptosis, the defining characteristic is a complete change in cellular morphology. As observed by electron microscopy, the cell undergoes shrinkage, chromatin margination, membrane blebbing, nuclear condensation and then segmentation, and division into apoptotic bodies which may be phagocytosed (11, 19, 24). The characteristic apoptotic bodies are short-lived and minute, and can resemble other cellular constituents when viewed by brightfield microscopy. DNA fragmentation in apoptotic cells is followed by cell death and removal from the tissue, usually within several hours (7). A rate of tissue regression as rapid as 25% per day can result from apparent apoptosis in only 2-3% of the cells at any one time (6). Thus, the quantitative measurement of an apoptotic index by morphology alone can be difficult.
DNA fragmentation is usually associated with ultrastructural changes in cellular morphology in apoptosis (26, 38).
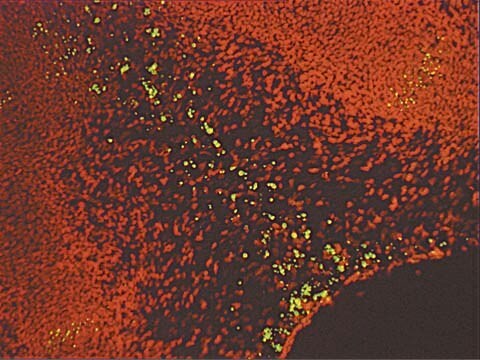
Another method for examining apoptosis via DNA fragmentation is by the TUNEL assay, (13) which is the basis of ApopTag technology. The DNA strand breaks are detected by enzymatically labeling the free 3′-OH termini with modified nucleotides. These new DNA ends that are generated upon DNA fragmentation are typically localized in morphologically identifiable nuclei and apoptotic bodies. In contrast, normal or proliferative nuclei, which have relatively insignificant numbers of DNA 3′-OH ends, usually do not stain with the kit. ApopTag Kits detect single-stranded (25) and double-stranded breaks associated with apoptosis. Drug-induced DNA damage is not identified by the TUNEL assay unless it is coupled to the apoptotic response (8). In addition, this technique can detect early-stage apoptosis in systems where chromatin condensation has begun and strand breaks are fewer, even before the nucleus undergoes major morphological changes (4, 8).
Apoptosis is distinct from accidental cell death (necrosis). Numerous morphological and biochemical differences that distinguish apoptotic from necrotic cell death are summarized in the following table (adapted with permission from reference 39). ApopTag In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kits distinguish apoptosis from necrosis by specifically detecting DNA cleavage and chromatin condensation associated with apoptosis. However, there may be some instances where cells exhibiting necrotic morphology may stain lightly (14, 29) or, in rare instances, DNA fragmentation can be absent or incomplete in induced apoptosis (11).
Since an understanding of cell morphology is critical for data interpretation and because of the potential for experimentally modifying or overcoming normal apoptotic controls, the following strategy is advised. When researching a new system, the staging and correlation of apoptotic morphology and DNA fragmentation should be characterized. In some tissues, cytoplasmic shrinkage may be indicated by a clear space surrounding the cell. The nuclear morphology of positive cells should be carefully observed at high magnification (400x-1000x). Early staged positive, round nuclei may have observable chromatin margination. Condensed nuclei of middle stages, and apoptotic bodies, usually are stained. Apoptotic bodies may be found either in the extracellular space or inside of phagocytic cells. It is highly recommended that less experienced observers should refer to illustrations of dying cells for comparison with new data (e.g. 11, 19, 24).
An additional, although far less sensitive, method of confirming ApopTag staining results is the detection of DNA fragmentation on agarose gels. If a large percent of the cells in the tissue are apoptotic, then electrophoresis of extracted total genomic DNA and standard dye staining can be used to corroborate the in situ staining. However, the single-cell sensitivity of ApopTag histochemistry is far higher than this method. DNA laddering data of comparable sensitivity may be obtained in several other ways. These include methods for selectively extracting the low molecular weight DNA (15), for preparing radiolabeled DNA (30, 40) in combination with resin-bed purification of DNA (12), and for DNA amplification by PCR (35).
The in situ staining of DNA strand breaks detected by the TUNEL assay and subsequent visualization by light microscopy gives biologically significant data about apoptotic cells which may be a small percentage of the total population (13, 16). Apoptotic cells stained positive with ApopTag Kits are easier to detect and their identification is more certain, as compared to the examination of simply histochemically stained tissues. Another feature of ApopTag is that quantitative results can be obtained using flow cytometry, since end-labeling methodology detects apoptotic cells with a >10-fold higher sensitivity than necrotic cells (14,17). In addition, the occurrence of DNA fragmentation with regard to the cell cycle phase of apoptotic cells can be examined using the TUNEL assay and flow cytometry (16,18).
This kit is designed for use on adherent and suspended cells. For tissue sections use our ApopTag kits Catalog Number S7110 or S7111.
In some instances, certain tissues contain cell types which bind any fluorescein labeled nucleotide such as that contained in the ApopTag Fluorescein Direct Kit (S7160). It is therefore recommended that this kit be used to stain cell suspensions, cytospins and cell cultures, but not tissue sections. Chemicon suggests the use of the ApopTag Fluorescein Kits (S7110, S7111) or the ApopTag Red Kit (S7165) for fluorescent staining tissue sections.
Application
ApopTag In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kits label apoptotic cells in research samples by modifying fragmented genomic DNA utilizing terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) for detection of positive cells by specific staining. This manual contains information and protocols for the ApopTag Fluorescein Direct In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit (Catalog number S7160).
Principles of the Procedure
The reagents provided in ApopTag Kits are designed to label the free 3′OH DNA termini in situ with chemically labeled and unlabeled nucleotides. The nucleotides contained in the Reaction Buffer are enzymatically added to the DNA by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) (13, 31). TdT catalyzes a template-independent addition of nucleotide triphosphates to the 3′-OH ends of double-stranded or single-stranded DNA. In the ApopTag Direct Methodology, the incorporated nucleotides form an oligomer composed of fluorescein nucleotide and unlabeled nucleotide in a random sequence. The ratio of labeled to unlabeled nucleotide in the kit is optimized to minimize fluorescein self-quenching.
Results using ApopTag Kits have been widely published (see Sec. V. References, Publications Citing ApopTag Kits). The ApopTag product line provides various options in experimental design. A researcher can choose to detect staining by brightfield or fluorescence microscopy or by flow cytometry, depending on available expertise and equipment. There are also opportunities to study other proteins of interest in the context of apoptosis when using ApopTag Kits. By using antibodies conjugated with an enzyme other than peroxidase and an appropriate choice of substrate, it is possible to simultaneously examine another protein and apoptosis using ApopTag Peroxidase Kits. There is also a choice of fluorophores (fluorescein and rhodamine) using ApopTag technology. Flexibility exists in choosing antibody-fluor combinations to study other important proteins.
Components
Storage and Stability
Disclaimer
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Carc. 1B - Eye Irrit. 2 - Muta. 2 - Repr. 1B - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT RE 2 Inhalation
Target Organs
Respiratory Tract
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible, acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service