79267
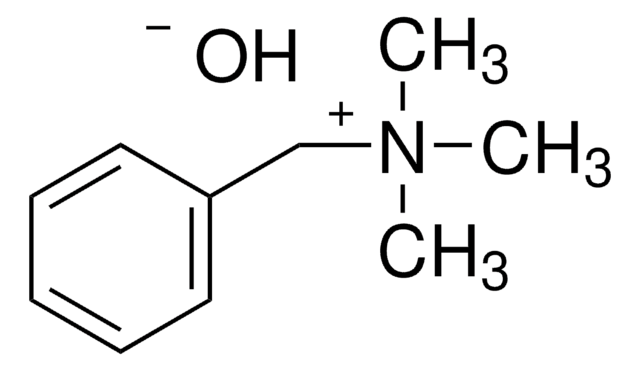
Trimethylphenylammonium hydroxide solution
~25% in H2O (1.68 M)
Synonym(s):
Phenyltrimethylammonium hydroxide, TMAH
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
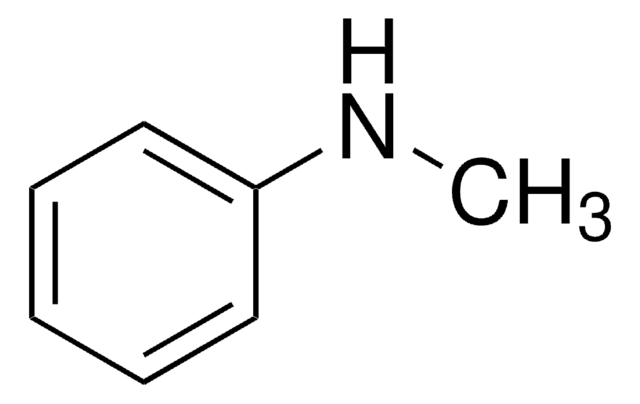
(CH3)3N(OH)C6H5
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
153.22
Beilstein:
3917033
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352005
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
form
liquid
concentration
~25% in H2O (1.68 M)
refractive index
n20/D 1.395
functional group
amine
SMILES string
[OH-].C[N+](C)(C)c1ccccc1
InChI
1S/C9H14N.H2O/c1-10(2,3)9-7-5-4-6-8-9;/h4-8H,1-3H3;1H2/q+1;/p-1
InChI key
HADKRTWCOYPCPH-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Trimethylphenylammonium hydroxide solution (TMPAH) is a quaternary ammonium compound that is commonly used as a strong base in organic synthesis. It is also used as a deprotecting agent for the removal of t-butoxycarbonyl (Boc) groups from amino acids or peptides and benzyl protecting groups from alcohols or amines.
Application
Trimethylphenylammonium hydroxide solution can be used to initiate the polymerization of the monomer 1,8-dihydroxymethyl-1,3,5,7-octatetrayne (DHOT) for the preparation of polymer nanospheres. It is also used as a base in the synthesis of alkyl 3-nitroacrylates via aldol reaction with nitroacetaldehyde or nitroacetone.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class Code
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Fazel Abdolahpur Monikh et al.
Nature communications, 12(1), 899-899 (2021-02-11)
Analytical limitations considerably hinder our understanding of the impacts of the physicochemical properties of nanomaterials (NMs) on their biological fate in organisms. Here, using a fit-for-purpose analytical workflow, including dosing and emerging analytical techniques, NMs present in organisms are characterized
R W Gullick et al.
Environmental science & technology, 35(7), 1523-1530 (2001-05-12)
A natural shale and four synthetic organoclays were compared as potential sorbent additives to containment barriers at hazardous waste sites. Trimethylphenyl ammonium bentonite (TMPA-bent) was shown in batch experiments to have the greatest sorption capacities for 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene, trichloroethylene, and methyl
Jeffrey T Auletta et al.
Chemico-biological interactions, 187(1-3), 135-141 (2010-05-25)
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) contains a narrow and deep active site gorge with two sites of ligand binding, an acylation site (or A-site) at the base of the gorge and a peripheral site (or P-site) near the gorge entrance. The P-site contributes
Anthony A Mikulec et al.
Otology & neurotology : official publication of the American Otological Society, American Neurotology Society [and] European Academy of Otology and Neurotology, 30(2), 131-138 (2009-01-31)
Drugs applied to the middle ear enter perilymph through the bony otic capsule. Drugs applied intratympanically in humans are thought to enter the cochlea primarily through the round window membrane (RWM). Local drug treatments of the ear are commonly evaluated
Alec N Salt et al.
Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology : JARO, 13(6), 771-783 (2012-09-13)
Perilymph pharmacokinetics was investigated by a novel approach, in which solutions containing drug or marker were injected from a pipette sealed into the perilymphatic space of the lateral semi-circular canal (LSCC). The cochlear aqueduct provides the outlet for fluid flow
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service