62141
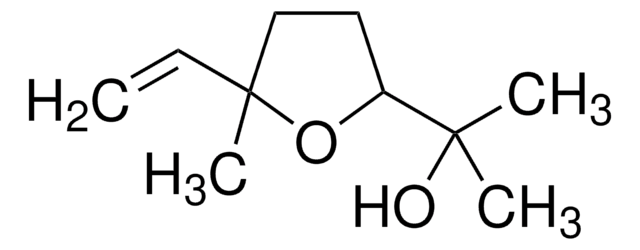
Linalool oxide
mixture of isomers, ≥97.0% (GC)
Synonym(s):
2-(5-Methyl-5-vinyltetrahydro-1-furyl)-2-propanol
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
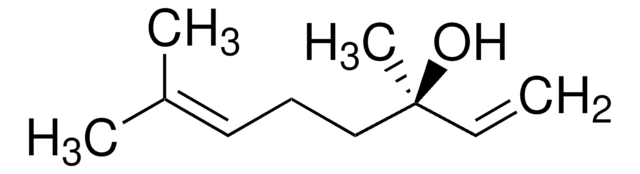
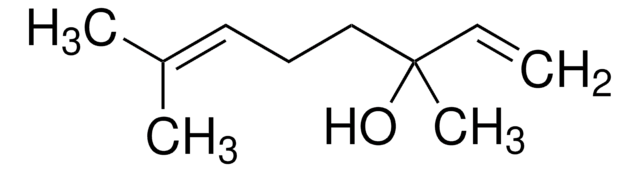
C10H18O2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
170.25
Beilstein:
117527
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Assay
≥97.0% (GC)
density
0.945 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.)
functional group
ether
SMILES string
CC(C)(O)C1CCC(C)(O1)C=C
InChI
1S/C10H18O2/c1-5-10(4)7-6-8(12-10)9(2,3)11/h5,8,11H,1,6-7H2,2-4H3
InChI key
BRHDDEIRQPDPMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Linalool oxide is a monoterpenoid compound, commonly found in some species of the aromatic plants. It can be obtained from linalool either by oxidation or via biotransfomation using the fungus Aspergillus niger. It is always present as a mixture of both cis and trans forms.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class Code
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
163.4 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
73 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Apsimon J
Total Synthesis of Natural Products, 2 (2009)
"Anxiolytic-like effects of inhaled linalool oxide in experimental mouse anxiety models"
Souto-Maior NF, et al.
Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior, 100(02), 259-263 (2011)
Paroma Mitra et al.
Pest management science, 77(1), 285-299 (2020-07-23)
The viviparous aphid Aphis craccivora Koch (Hemiptera: Aphididae) is a serious threat to the crop yield of Lathyrus sativus L. (Fabaceae), commonly known as grass pea. The synthetic insecticides applied to control this insect pest are not safe for the
Vincent O Nyasembe et al.
Parasites & vectors, 8, 581-581 (2015-11-11)
Lack of effective vaccines and therapeutics for important arboviral diseases such as Rift Valley fever (RVF) and dengue, necessitates continuous monitoring of vector populations for infections in them. Plant-based lures as surveillance tools has the potential of targeting mosquitoes of
Bao-Ting Yu et al.
Parasites & vectors, 8, 598-598 (2015-11-19)
Most mosquito species need to obtain sugar from host plants. Little is known about the chemical cues that Culex pipiens pallens use during their orientation to nectar host plants. In this study, we investigated the behavioural responses of female Cx.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service