All Photos(1)
About This Item
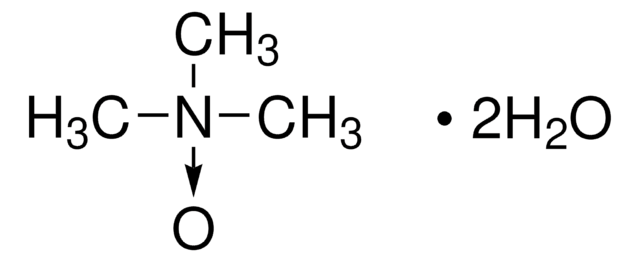
Linear Formula:
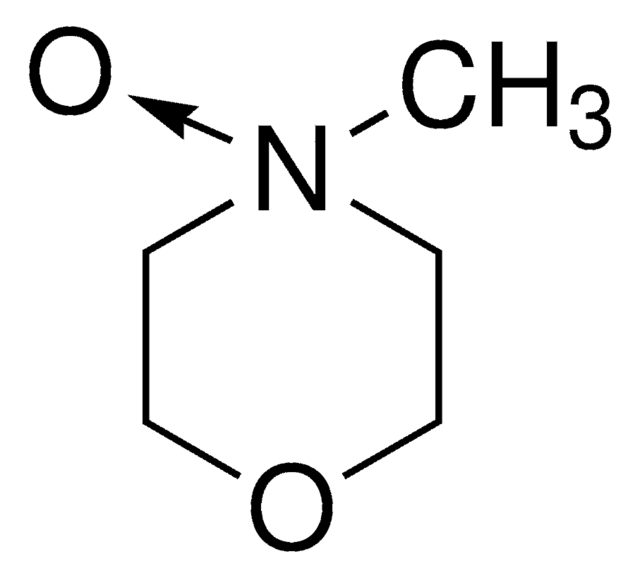
(CH3)3N(O)
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
75.11
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352116
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
95%
reaction suitability
reagent type: oxidant
mp
220-222 °C (lit.)
functional group
amine
SMILES string
C[N+](C)(C)[O-]
InChI
1S/C3H9NO/c1-4(2,3)5/h1-3H3
InChI key
UYPYRKYUKCHHIB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Trimethylamine N-oxide is an organic compound that belongs to the class of amine oxides. It is generally found in the tissues of marine organisms, wherein it helps protect them from harsh conditions like salinity, hydrostatic pressure, temperature, and high urea.
Application
Trimethylamine N-oxide can be used:
- As a demetallation and decarbonylation reagent for organometallic compounds.
- To prepare azomethine ylide by reaction with lithium di-isopropylamide. This, in turn, may be reacted with simple alkenes to obtain corresponding pyrrolidines.
- To mediate the conversion of thiols to disulfides.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Journal of Organometallic Chemistry, 471, 241-241 (1994)
Trimethylamine N-oxide: the good, the bad and the unknown
Velasquez MT, et al.
Toxins, 8(11), 326-326 (2016)
Trimethylamine N-oxide as a precursor of azomethine ylides
Beugelmans R, et al.
Journal of the Chemical Society. Chemical Communications, 471(1), 31-32 (1983)
Demir Djekic et al.
Journal of the American Heart Association, 9(18), e016518-e016518 (2020-09-08)
Background A vegetarian diet (VD) may reduce future cardiovascular risk in patients with ischemic heart disease. Methods and Results A randomized crossover study was conducted in subjects with ischemic heart disease, assigned to 4-week intervention periods of isocaloric VD and
Site selectivity studies on heterobimetallic complexes: substitution reactions of (.eta.5-C5H5)MM'(CO)8 (M = Mo, W; M' = Mn, Re)
Ingham WL and Coville NJ
Inorganic Chemistry, 31(20), 4084-4090 (1992)
Articles
Magnetic nanoparticles have attracted tremendous attention due to their novel properties and their potential applications in magnetic recording, magnetic energy storage and biomedicine.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 317594-1G | 4061826692035 |
| 317594-5G | 4061826692066 |
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service