252573
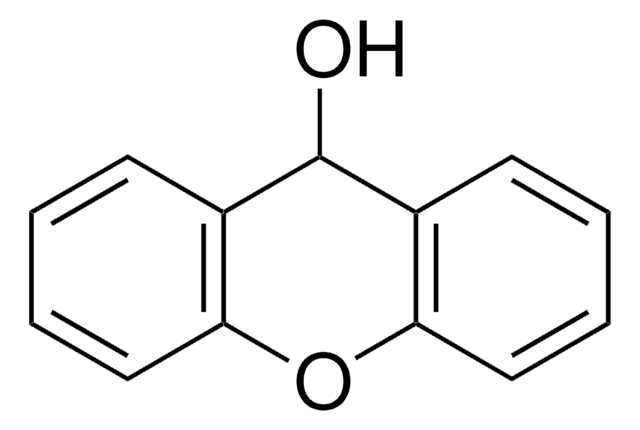
Xanthydrol
98%
Synonym(s):
9-Hydroxyxanthene, 9-Xanthenol
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C13H10O2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
198.22
Beilstein:
10395
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
98%
form
powder
mp
127-128 °C (lit.)
solubility
methanol: soluble 50 mg/mL, slightly hazy
functional group
hydroxyl
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
OC1c2ccccc2Oc3ccccc13
InChI
1S/C13H10O2/c14-13-9-5-1-3-7-11(9)15-12-8-4-2-6-10(12)13/h1-8,13-14H
InChI key
JFRMYMMIJXLMBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Xanthydrol is also known as 9H-xanthen-9-ol.
Application
Xanthydrol has been used as derivatization reagent in the determination of:
- acrylamide in surface and drinking water by GC-MS method
- urea by HPLC with fluorescence detection
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Hyun-Hee Lim et al.
Journal of separation science, 36(18), 3059-3066 (2013-07-10)
A sensitive GC-MS method has been established for the determination of acrylamide in surface and drinking water based on derivatization with xanthydrol. Deuterated acrylamide (acrylamide-d3 ) was chosen as the internal standard for analyzing the water sample. The derivatization of
P V Biles et al.
Journal of AOAC International, 81(6), 1155-1161 (1998-12-16)
Contamination of food and food packaging material by rodent urine is evidence of insanitary conditions. Urea from rodent urine is used as a chemical indicator of contamination. The limit of detection of the xanthydrol/urea AOAC Method 959.14 by formation of
Shona Clark et al.
Journal of chromatography. A, 1161(1-2), 207-213 (2007-06-16)
A high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method for the determination of urea that incorporates automated derivatisation with xanthydrol (9H-xanthen-9-ol) is described. Unlike the classic xanthydrol approach for the determination of urea, which involves the precipitation of dixanthylurea (N,N'-di-9H-xanthen-9-ylurea), the derivatisation procedure
Kumiko Yamazaki et al.
Food additives & contaminants. Part A, Chemistry, analysis, control, exposure & risk assessment, 29(5), 705-715 (2012-01-20)
A novel GC-MS method was developed for the determination of acrylamide, which is applicable to a variety of processed foods, including potato snacks, corn snacks, biscuits, instant noodles, coffee, soy sauces and miso (fermented soy bean paste). The method involves
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service