All Photos(1)
About This Item
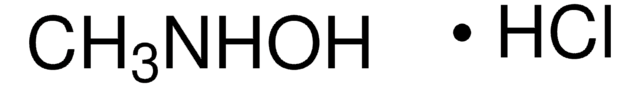
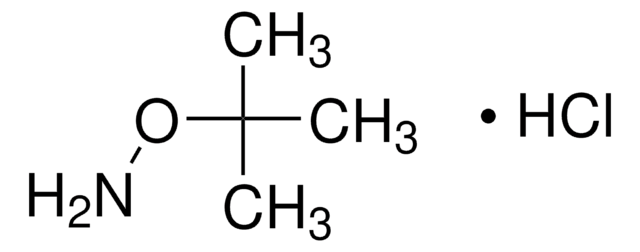
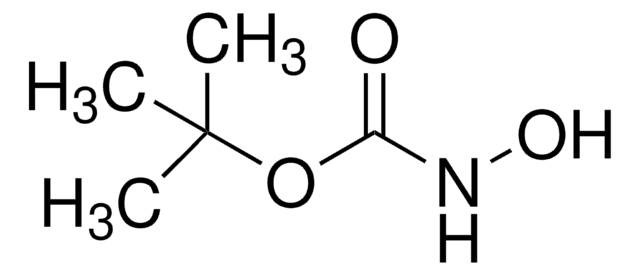
Linear Formula:
(CH3)3CNHOH · HCl
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
125.60
Beilstein:
3546053
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Assay
≥98%
form
solid
mp
183-185 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
Cl.CC(C)(C)NO
InChI
1S/C4H11NO.ClH/c1-4(2,3)5-6;/h5-6H,1-3H3;1H
InChI key
DCSATTBHEMKGIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
N-tert-Butylhydroxylamine hydrochloride was used in spin trapping of short-lived radicals. It was also used in the synthesis of α-ketoamides and 3-spirocyclopropanated 2-azetidinones.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Yu-Kyung Kim et al.
Clinical hemorheology and microcirculation, 40(4), 315-324 (2009-01-08)
Irradiation has been shown to induce biochemical changes in stored red blood cells (RBCs) and to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS). This study evaluated the hemorheological properties, the degree of lipid peroxidation and the oxidative susceptibility of irradiated RBCs. Furthermore
Hyun Jeong Kim et al.
Redox report : communications in free radical research, 10(6), 287-293 (2006-01-28)
Heat shock may increase oxidative stress due to increased production of reactive oxygen species and/or the promotion of cellular oxidation events. Therefore, compounds that scavenge reactive oxygen species may regulate heat shock-induced cell death. Recently, it has been shown that
Jin Hyup Lee et al.
Carcinogenesis, 25(8), 1435-1442 (2004-03-16)
Exposure of cells to ionizing radiation leads to formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that are associated with radiation-induced cytotoxicity. Therefore, compounds that scavenge ROS may confer radioprotective effects. Recently, it has been shown that the decomposition product of the
David W Killilea et al.
Antioxidants & redox signaling, 5(5), 507-516 (2003-10-29)
Iron accumulates as a function of age in several tissues in vivo and is associated with the pathology of numerous age-related diseases. The molecular basis of this change may be due to a loss of iron homeostasis at the cellular
On the anti-aging activities of aminoguanidine and N-t-butylhydroxylamine.
A R Hipkiss
Mechanisms of ageing and development, 122(2), 169-171 (2001-02-13)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service