170925
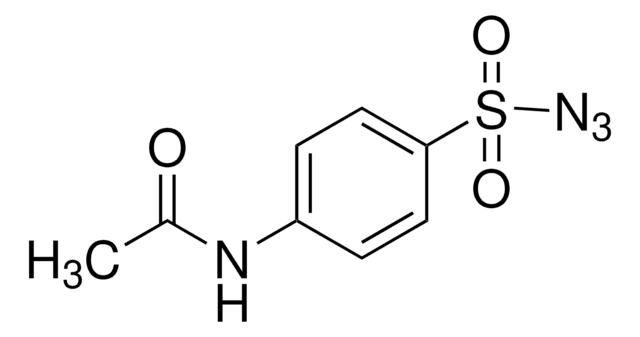
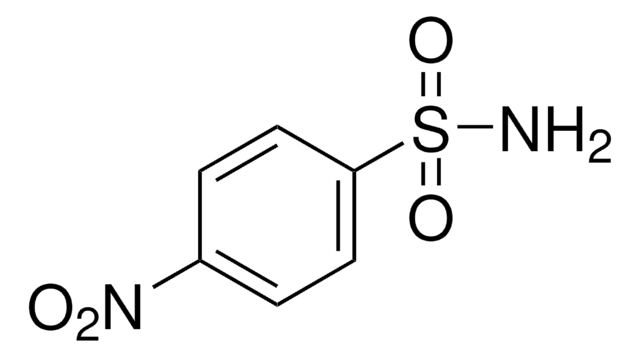
4-Nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride
technical grade, 90%
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
O2NC6H4SO2Cl
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
221.62
Beilstein:
746543
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
grade
technical grade
Assay
90%
mp
66-70 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
[O-][N+](=O)c1ccc(cc1)S(Cl)(=O)=O
InChI
1S/C6H4ClNO4S/c7-13(11,12)6-3-1-5(2-4-6)8(9)10/h1-4H
InChI key
JXRGUPLJCCDGKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
4-Nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride was used in the synthesis of [Cu(bipy)2Cl](nbs) where bipy = 2,2′-bipyridine, nbs = 4-nitrobenzenesulfonate. It was also used to determine estrogens in biological fluids.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1 - Repr. 2 - Skin Sens. 1A
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Tatsuya Higashi et al.
Analytical and bioanalytical chemistry, 386(3), 658-665 (2006-04-13)
A practical procedure for determining estrogens in biological fluids has been studied using liquid chromatography-electron capture atmospheric pressure chemical ionization-mass spectrometry combined with derivatization. Among the commercially available reagents (4-nitrobenzoyl chloride, 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene, 4-nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride and 4-nitrobenzyl bromide), 4-nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride was
Mahboubeh A Sharif et al.
Acta chimica Slovenica, 59(2), 289-293 (2012-06-01)
[Cu(bipy)2Cl](nbs) (1) (bipy = 2,2'-bipyridine, nbs = 4-nitrobenzenesulfonate) was obtained from the reaction of 4-nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride and 2-amine-4-methylopyridine with CuCl2 in the presence of 2,2'-bipyridine and characterized by elemental analysis, IR spectra and X-ray single-crystal diffraction. The asymmetric unit of
Tsurng-Juhn Huang et al.
European journal of medicinal chemistry, 90, 428-435 (2014-12-03)
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a causative reagent that frequently causes progressive liver diseases, leading to the development of acute, chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and eventually hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Despite several antiviral drugs including interferon-α and nucleotide derivatives are approved for
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service