Kluczowe dokumenty
SBR00044
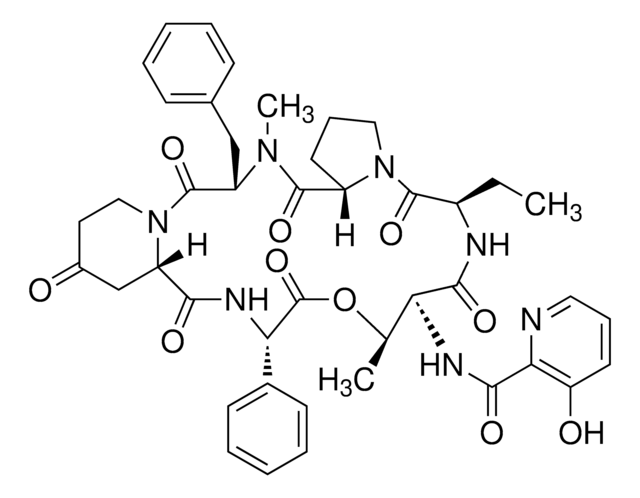
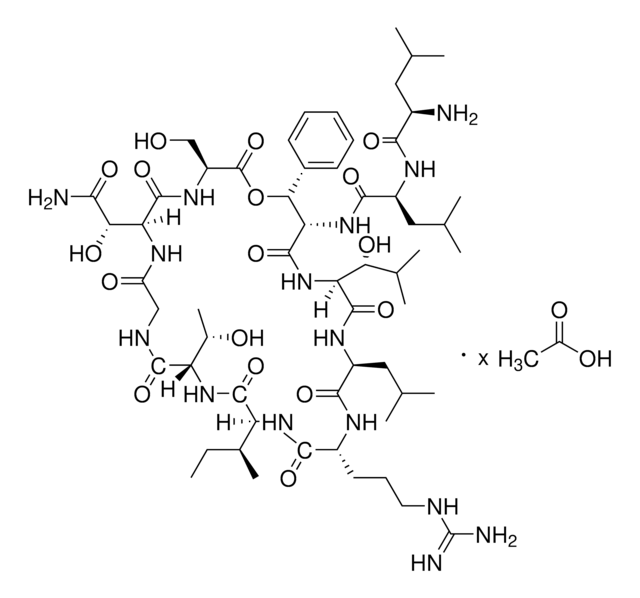
Pristinamycin
≥98% (Assay)
Synonim(y):
Prystynamycyna
Wybierz wielkość
Wybierz wielkość
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Poziom jakości
Próba
≥98% (Assay)
Formularz
powder
kolor
white to faint yellow
spektrum działania antybiotyku
Gram-positive bacteria
Tryb działania
protein synthesis | inhibits
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
ciąg SMILES
CN(C)C1=CC=C(C[C@@H](C(N2CCC(C[C@H]2C(N[C@@H](C3=CC=CC=C3)C(O[C@H](C)[C@H](NC(C4=NC=CC=C4O)=O)C5=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)N(C)C([C@H]6N(C([C@@H](N5)CC)=O)CCC6)=O)C=C1.O=C(N7C(C(O[C@H](C(C)C)[C@H](C)/C=C/C(NC/C=C/C(C)=C/[C@@H](O)CC(C8)=O)=O)=O)=CCC7)C9=COC8=N9
InChI
1S/C45H54N8O10.C28H35N3O7/c1-6-31-42(59)52-22-11-14-32(52)43(60)51(5)34(24-27-16-18-29(19-17-27)50(3)4)44(61)53-23-20-30(54)25-33(53)39(56)49-37(28-12-8-7-9-13-28)45(62)63-26(2)36(40(57)47-31)48-41(58)38-35(55)15-10-21-46-38;1-17(2)26-19(4)9-10-24(34)29-1
Klucz InChI
YVMBAUWDIGJRNY-OOVQIFRISA-N
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
- w klonowaniu i sekwencjonowaniu genów zaangażowanych w biosyntezę antybiotyków depsipeptydowych pristinamycyn I (PI) produkowanych przez Streptomyces pristinaespiralis
- w badaniach nad indukowalnym systemem ekspresji genów u mykobakterii
Działania biochem./fizjol.
- Hamowanie syntezy białek: Prystynamycyna wiąże się z podjednostką rybosomalną 50S w komórkach bakteryjnych, hamując w ten sposób tworzenie wiązań peptydowych podczas syntezy białek. Zakłóca to proces translacji i zapobiega produkcji podstawowych białek niezbędnych do wzrostu i przeżycia bakterii.
- Zakłócenie syntezy ściany komórkowej: Prystynamycyna zakłóca również syntezę ścian komórkowych bakterii. Hamuje etap transpeptydacji biosyntezy peptydoglikanu, który jest niezbędny do sieciowania składników ściany komórkowej. Prowadzi to do osłabienia ściany komórkowej bakterii i ostatecznej lizy komórek
Spektrum działania: Prystynamycyna wykazuje aktywność przeciwbakteryjną przeciwko bakteriom Gram-dodatnim, takim jak Staphylococcus spp. i Streptococcus spp. Prystynamycyna wykazuje aktywność przeciwdrobnoustrojową przeciwko zakażeniom Mycoplasma genitalium opornym na makrolidy.
Cechy i korzyści
- Szerokie spektrum działania: Prystynamycyna jest skuteczna wobec szerokiego zakresu bakterii, w tym zarówno bakterii Gram-dodatnich, jak i Gram-ujemnych, a także szczepów opornych.
- Działanie synergistyczne: Dwa składniki prystyramycyny działają razem, dając efekt synergistyczny, co oznacza, że razem są bardziej skuteczne niż osobno.
- Wszechstronność: Pristinamycyna może być stosowana w biologii komórkowej i zastosowaniach biochemicznych
Inne uwagi
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Dokumenty section.
Proszę o kontakt, jeśli potrzebna jest pomoc Obsługa Klienta
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej