G3042
Anti-GAL4 DNA-BD antibody produced in rabbit
affinity isolated antibody, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
Anti-Galactose 4 DNA Binding Domain
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
affinity isolated antibody
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
technique(s)
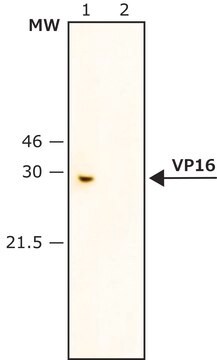
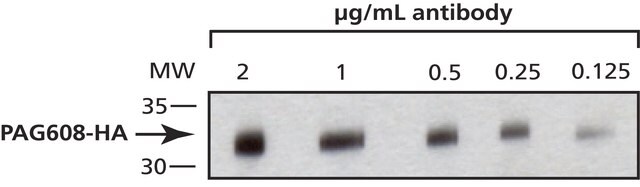
western blot: 1-2 μg/mL using GAL4 (DBD 1-147) fusion protein
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
General description
The polyclonal Anti-GAL4 DNA-BD rabbit antibody is a synthetic peptide that recognizes GAL4 DNA binding domain fusion proteins. GAL4 protein is an 881 amino acid transcription factor. It contains functionally independent N-terminal DNA binding (147 amino acids) and C-terminal activator domains. It is a constituent of yeast two hybrid system, where GAL 4 DNA-BD is fused to protein X (bait) and GAL4 activation domain is fused to protein Y (prey).
Specificity
Anti-GAL4 DNA-BD recognizes GAL4 DNA binding domain fusion proteins.
Immunogen
synthetic peptide corresponding to the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL4 protein DNA binding domain (amino acids 39-52).
Application
Anti-GAL4 DNA-BD antibody produced in rabbit has been used in western blotting.
Biochem/physiol Actions
GAL4 transcription factor is involved in the induction of genes that regulate galactose metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The yeast two hybrid system is widely used for the characterization of domains that are necessary and sufficient for the interaction of two known proteins by deletion and mutational analysis.
Physical form
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 1% bovine serum albumin and 15 mM sodium azide.
Storage and Stability
For continuous use store at 2-8°C for up to one month. For extended storage, freeze in working aliquots at –20 °C. Repeated freezing and thawing, or storage in “frost-free” freezers, is not recommended. If slight turbidity occurs upon prolonged storage, clarify the solution by centrifugation before use. Working dilution samples should be discarded if not used within 12 hours.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog, our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
nwg
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Sirtuin 7-dependent deacetylation of DDB1 regulates the expression of nuclear receptor TR4
Karim Mdf, et al.
Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 490(2), 423-428 (2017)
The putative SWI/SNF complex subunit BRAHMA activates flower homeotic genes in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Lidia Hurtado et al.
Plant molecular biology, 62(1-2), 291-304 (2006-07-18)
Arabidopsis thaliana BRAHMA (BRM, also called AtBRM) is a SNF2 family protein homolog of Brahma, the ATPase of the Drosophila SWI/SNF complex involved in chromatin remodeling during transcription. Here we show that, in contrast to its Drosophila counterpart, BRM is
Yukiko Imai et al.
Chromosoma, 126(6), 681-695 (2017-05-21)
PR domain-containing protein 9 (PRDM9) is a major regulator of the localization of meiotic recombination hotspots in the human and mouse genomes. This role involves its DNA-binding domain, which is composed of a tandem array of zinc fingers, and PRDM9-dependent
Mitsuki Uemura et al.
Veterinary and comparative oncology, 18(2), 247-255 (2019-09-14)
RAD51 forms a complex with BRCA2 and plays a central role in the DNA damage response pathway that is associated with homologous recombination. The structures of RAD51 and its homologues are highly conserved from prokaryotes to higher eukaryotes. Although a
X Wang et al.
Oncogene, 27(13), 1894-1904 (2007-10-02)
As a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p16(INK4a) plays a key role in cell cycle progression and cellular differentiation, and its expression is frequently altered in human cancers through epigenetically mediated transcriptional silencing. In this report, we demonstrate that p300 was able
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service