MABN1817
Anti-α-Synuclein Antibody, clone 2F12
clone 2F12, from mouse
Synonym(s):
Alpha-synuclein, NACP, Non-A beta component of AD amyloid, Non-A4 component of amyloid precursor, Synuclein alpha-140
About This Item
ICC
IHC
IP
WB
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable (paraffin)
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
western blot: suitable
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
2F12, monoclonal
species reactivity
rat, human, mouse
technique(s)
ELISA: suitable
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable (paraffin)
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
western blot: suitable
isotype
IgG2bκ
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
ambient
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... SNCA(6622)
General description
Specificity
Immunogen
Application
ELISA Analysis: A representative lot (0.4 µL in 30 µL buffer/well for coating) captured recombinant human α-synuclein (0.2-40 ng/mL) in a sandwich ELISA application utilizing clone SOY1 (Cat. No. MABN1818; preconjugated with Sulfo tag) as the detection antibody (Courtesy of Tim Bartels, Ph.D., Brigham and Women′s Hospital, Boston, MA, U.S.A.).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A 1:1,000 dilution from a representative lot immunostained primary mouse cortical neurons (Courtesy of Tim Bartels, Ph.D., Brigham and Women′s Hospital, Boston, MA, U.S.A.).
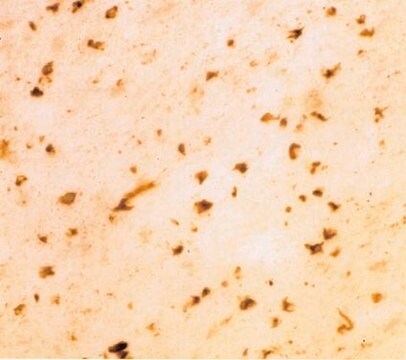
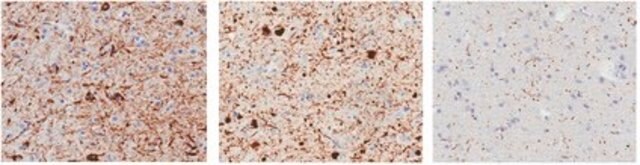
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A 1:11,110 dilution from a representative lot immunostained Lewy bodies (LBs) in striatum tissue sections from Parkinson′s diseased (PD) human brain (Courtesy of Tim Bartels, Ph.D., Brigham and Women′s Hospital, Boston, MA, U.S.A.).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: 4 µL from a representative lot immunoprecipitated α-synuclein from 50 µg of HEL human erythroleukemia cell lysate (Courtesy of Tim Bartels, Ph.D., Brigham and Women′s Hospital, Boston, MA, U.S.A.).
ELISA Analysis: A representative lot captured both endogenous α-synuclein (αS) from human cortical homogenate, as well the exogenously expressed wild type and familial PD (fPD) αS mutants (A30P, E46K, H50Q, G51D, A53T) from sytosolic extracts of transfected M17D human neuroblastoma cells in a sandwich ELISA application utilizing clone SOY1 (Cat. No. MABN1818; preconjugated with Sulfo tag) as the detection antibody (Dettmer, U., et al. (2015). Nat. Commun. 6:7314).
ELISA Analysis: A representative lot captured both pre-aggregated fibrillar recombinant α-synuclein as well as partially purified Lewy bodies (LBs) from a DLB (dementia with LBs) patient with or without prior sample denaturing by boiling with 2% SDS in a sandwich ELISA application utilizing clone SOY1 (Cat. No. MABN1818; preconjugated with Sulfo tag) as the detection antibody (Dettmer, U., et al. (2015). Nat. Commun. 6:7314).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected cytosolic localization of endogenous rat α-synuclein (αS) and exogenously overexpressed human αS by fluorescent immunocytochemistry staining of 4% paraformaldehyde-fixed, 0.25% Triton X-100-permeabilized primary rat neurons and transfected M17D human neuroblastoma cells (Dettmer, U., et al. (2015). Nat. Commun. 6:7314).
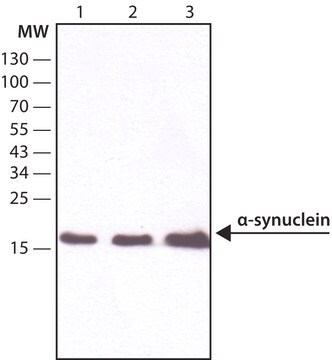
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected monomeric α-synuclein (αS) as well as αS multimers (αS60, αS80 and αS100) in extract from disuccinimidyl glutarate (DSG) cross-linked mouse brain bits, human iPSCs (both S A53T mutant and corrected isogenic line) and ESCs (both wild-type and genetically engineered isogenic αS E46K line). A significantly reduced αS60 level was seen with A53T and E46K mutants (Dettmer, U., et al. (2015). Nat. Commun. 6:7314).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected monomeric α-synuclein (αS) as well as αS multimers (αS60, αS80 and αS100) in cytosolic extracts from disuccinimidyl glutarate (DSG) cross-linked primary rat neurons, as well as human HEL erythroid leukemia and M17D neuroblastoma cells (Dettmer, U., et al. (2013). J. Biol. Chem. 288(9):6371-6385).
Neuroscience
Quality
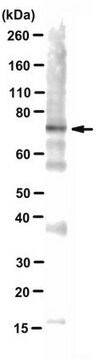
Western Blotting Analysis: A 1:1,000 dilution of this antibody detected α-synuclein in 10 µg of human fetal brain tissue lysate.
Target description
Physical form
Storage and Stability
Other Notes
Disclaimer
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
recommended
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service