MABF1495Z
Anti-NK1.1 (mouse) Antibody, clone PK136, Azide Free
clone PK136, from mouse
Synonym(s):
Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily B member 1B allele A, Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily B member 1C, CD161b, CD161c, CD161 antigen-like family member B, CD161 antigen-like family member C, Ly-55b, Ly-55c, Lymphocyte antigen 55b, Lymph
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
PK136, monoclonal
species reactivity
mouse
technique(s)
activity assay: suitable
flow cytometry: suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
isotype
IgG2aκ
GenBank accession no.
NCBI accession no.
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
mouse ... Klrb1C(17059)
General description
Specificity
Immunogen
Application
Activity Assay: A representative lot activated target cell killing by cross-linking NK cell surface NK1.1 (NKR-P1C) and target cell surface Fc receptor. Ab-induced redirected lysis (AIRL) assay employing NK cells expressing both NKR-P1B and NKR-P1C prevented NK cell cytotoxicity activation by clone PK136 (Carlyle, J.R., et al. (1999). J. Immunol. 162(10):5917-5923).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot co-immunoprecipitated SHP-1, but not SHP-2 or SHIP, from Swiss NIH mouse-derived MNK-1 pre-NK cells upon upregulating NKR-P1B intracellular ITIM motif tyrosine phosphorylation by pervanadate treatment (Carlyle, J.R., et al. (1999). J. Immunol. 162(10):5917-5923).
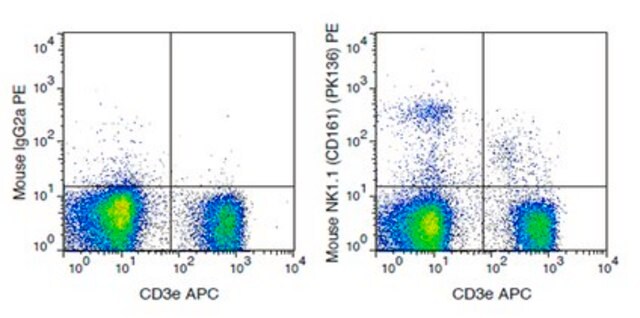
Flow Cytometry Analysis: A representative lot immunostained the surface of Jurkat transfectants expressing C57BL/6J (B6) mouse-derived NKR-P1B/CD161b or Swiss NIH (Sw) mouse-derived NKR-P1C/CD161c/NK1.1, but not Jurkat transfectants expressing B6-derived NKR-P1A/CD161a (Carlyle, J.R., et al. (1999). J. Immunol. 162(10):5917-5923).
Flow Cytometry Analysis: A representative lot immunostained NKR-P1B/CD161b-expressing NK cells from Swiss NIH (Sw) mouse strain, NKR-P1C/CD161c/NK1.1-expressing NK cells from C57BL/6J (B6), as well as (B6 3 Sw)F1 cross-strain-derived NK cells expressing both NKR-P1B and NKR-P1C (Carlyle, J.R., et al. (1999). J. Immunol. 162(10):5917-5923).
Note: Clone PK136 is also available in the following conjugated forms for flow cytometry application, APC (MABF1487 & MABF1488), FITC (MABF1489 & MABF1490), PE (MABF1491), PerCP-Cy5.5 (MABF1493 & MABF1494). redFluor® 710 (MABF1496 & MABF1497).
Inflammation & Immunology
Immunological Signaling
Quality
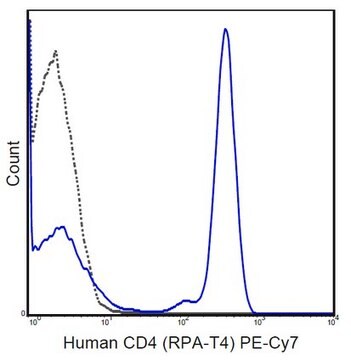
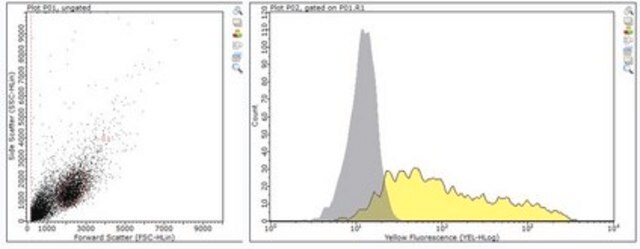
Flow Cytometry Analysis: 1.0 µg of this antibody detected NK1.1-positive mouse splenocytes.
Target description
Physical form
Storage and Stability
Handling Recommendations: Upon receipt and prior to removing the cap, centrifuge the vial and gently mix the solution. Aliquot into microcentrifuge tubes and store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles, which may damage IgG and affect product performance.
Other Notes
Legal Information
Disclaimer
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service