560596
PEDOT:PSS
low-conductivity grade, 2.7 wt. % aqueous dispersion
Synonym(s):
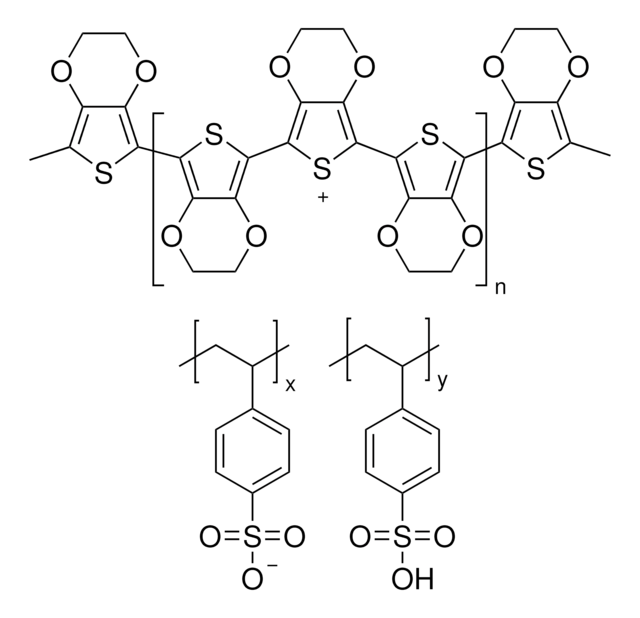
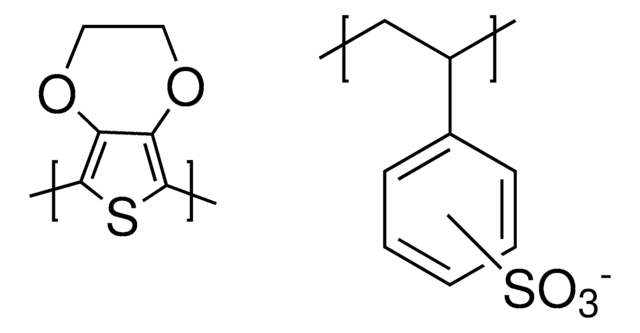
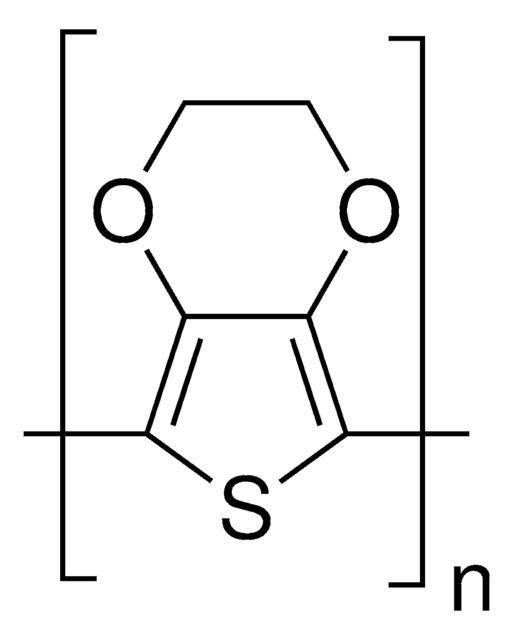
PEDOT:PSS, Poly(2,3-dihydrothieno-1,4-dioxin)-poly(styrenesulfonate)
About This Item
Recommended Products
product name
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrenesulfonate), 2.7 wt % dispersion in H2O, low-conductivity grade
grade
low-conductivity grade
Quality Level
composition
PEDOT content, ~0.14%
PSS content, ~2.6%
concentration
2.7 wt % dispersion in H2O
impurities
<300 ppm Na
particle size
<200 nm, coeff var >95%
pH
1.2-1.8
conductivity
~1E-5 S/cm
viscosity
<20 cP(20 °C)
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Features and Benefits
Packaging
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1
Storage Class Code
8B - Non-combustible corrosive hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Tutorial Lithography Nanopatterning at Sigma-Aldrich. Lithography, based on traditional ink-printing techniques, is a process for patterning various layers, such as conductors, semiconductors, or dielectrics, on a surface.
New conducting and semiconducting polymers for plastic electronics
Find advantages of inorganic interface layer inks for organic electronic & other applications.
Conducting polymers such as polyaniline, polythiophene and polyfluorenes are now much in the spotlight for their applications in organic electronics and optoelectronics.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service