15149
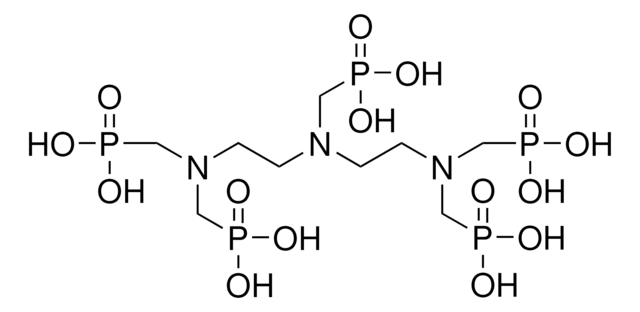
N,N-Bis(phosphonomethyl)glycine
≥98.0% (T)
Synonym(s):
N-(Carboxymethyl)iminodi(methylphosphinic acid), Glyphosine
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C4H11NO8P2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
263.08
Beilstein:
1884944
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥98.0% (T)
functional group
amine
carboxylic acid
SMILES string
O=P(CN(CP(O)(O)=O)CC(O)=O)(O)O
InChI
1S/C4H11NO8P2/c6-4(7)1-5(2-14(8,9)10)3-15(11,12)13/h1-3H2,(H,6,7)(H2,8,9,10)(H2,11,12,13)
InChI key
OXHDYFKENBXUEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
N,N-Bis(phosphonomethyl)glycine was present in the ligand bound to human apotransferrin.
Application
Application: Complexing agent; pK-values: pK1: ·2, pK2: 2.0, pK3: 5.20, pK4: 6.77, pK5: 10.89
Anti-diabetic; delay onset of diabetes in non-obese NOD mice
Glyphosine binds to a pocket of MHC class II molecules I-Ag7 and DQ8, and modify T cell responses to the autoantigenic insulin B chain fragment 9–23 (B:9–23) peptide. Glyphosine stimulate IL-10 production and delay onset of diabetes in non-obese NOD mice.†
Anti-diabetic; delay onset of diabetes in non-obese NOD mice
Glyphosine binds to a pocket of MHC class II molecules I-Ag7 and DQ8, and modify T cell responses to the autoantigenic insulin B chain fragment 9–23 (B:9–23) peptide. Glyphosine stimulate IL-10 production and delay onset of diabetes in non-obese NOD mice.†
Biochem/physiol Actions
Anti-diabetic; delay onset of diabetes in non-obese NOD mice
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1
Storage Class Code
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Aaron W Michels et al.
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 187(11), 5921-5930 (2011-11-02)
Class II major histocompatibility molecules are the primary susceptibility locus for many autoimmune disorders, including type 1 diabetes. Human DQ8 and I-A(g7), in the NOD mouse model of spontaneous autoimmune diabetes, confers diabetes risk by modulating presentation of specific islet
Markus Galanski et al.
Journal of medicinal chemistry, 46(23), 4946-4951 (2003-10-31)
A series of osteotropic (bone-seeking) [(bis(phosphonomethyl)amino-kappaN)acetato-kappaO(2-)]platinum(II) complexes attached to diammine, ethane-1,2-diamine, cis-R,S-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine, trans-S,S-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine, or trans-R,R-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine has been synthesized in accord with the concept of drug targeting and characterized by elemental analysis, (1)H, (13)C, and (31)P NMR spectroscopy. The in vitro
C T Bailey et al.
Biochemistry, 36(33), 10105-10108 (1997-08-19)
The mechanism by which the iron-transport protein transferrin releases its iron in vivo is presently unclear. In vitro studies have implicated two concurrent chelator-mediated iron-release pathways: one which is hyperbolic in nature, involving a conformational change in the protein as
W R Harris et al.
Biochemistry, 30(28), 6930-6936 (1991-07-16)
Difference ultraviolet spectroscopy has been used to monitor the binding of a series of phosphonate ligands to human apotransferrin. The ligands consist of pyrophosphate as well as the phosphonic acids (aminomethyl)phosphonic acid (AMPA), (hydroxymethyl)phosphonic acid (HMP), (phosphonomethyl)-iminodiacetic acid (PIDA), N,N-bis(phosphonomethyl)glycine
L J Olson et al.
Toxicology, 30(2), 103-114 (1984-03-01)
Exposure to the plant growth regulators, chlorocholine chloride (CCC) and glyphosine (GPS), resulted in significant immunomodulatory effects after feeding to deer mice (Peromyscus maniculatus) for 28 days. Cyclophosphamide (CP) and saline controls were included. Both CCC and GPS feeding levels
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service