S0439
SUMO-1 human
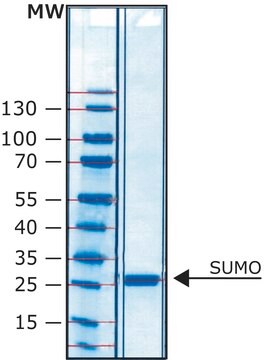
≥95% (SDS-PAGE), recombinant, expressed in E. coli (GST-tagged)
Synonym(s):
Sentrin-1
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
recombinant
expressed in E. coli (GST-tagged)
Quality Level
Assay
≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
mol wt
38.5 kDa
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−70°C
Gene Information
human ... SUMO1(7341)
General description
Small ubiquitin-like modifier 1 (SUMO-1), a protein, is one of the 5 SUMO paralogs expressed in mammalian cells with a low but significant homology with ubiquitin. This SUMO-1-GST fusion protein is produced from a DNA sequence corresponding to human SUMO-1 fused to a glutathione S-transferase (GST)-tag and is expressed in E. coli cells.
Application
SUMO-1 human has been used in pre-absorption for negative immunostaining to confirm the specificity of the small ubiquitin like modifier 1 (SUMO-1) antibody.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Small ubiquitin-like modifier 1 (SUMO-1) plays a key role in modulating survival, migration, and signal transduction in some cell lines. It can prevent in vitro migration and invasion of RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs). Higher expression of SUMO-1 may result in joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Conjugated to a variety of proteins by UbcH9, including RanGAP1, IκBα, and PML without the requirement of an equivalent E3 ubiquitin ligase.
Physical form
Solution in 50 mM HEPES, pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl and 1 mM DTT.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Small ubiquitin-related modifier paralogs are indispensable but functionally redundant during early development of zebrafish.
Yuan, et al.
Cell research, 20, 185-196 (2010)
J M Desterro et al.
Molecular cell, 2(2), 233-239 (1998-09-12)
Activation of NF-kappaB is achieved by ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation of IkappaBalpha. We have detected modified IkappaBalpha, conjugated to the small ubiquitin-like protein SUMO-1, which is resistant to signal-induced degradation. In the presence of an E1 SUMO-1-activating enzyme, Ubch9 conjugated
J M Desterro et al.
FEBS letters, 417(3), 297-300 (1997-12-31)
Ubiquitin conjugating enzymes participate in the thioester cascade that leads to protein ubiquitination. Although Ubc9 is homologous to E2 ubiquitin conjugating enzymes we have shown that it is unable to form a thioester with ubiquitin, but can form a thioester
Masaki Akita et al.
Scientific reports, 5, 10984-10984 (2015-06-05)
The xeroderma pigmentosum group C (XPC) protein complex is a key factor that detects DNA damage and initiates nucleotide excision repair (NER) in mammalian cells. Although biochemical and structural studies have elucidated the interaction of XPC with damaged DNA, the
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service