L2254
Lipoprotein Lipase from bovine milk
ammonium sulfate suspension, ≥2,000 units/mg protein (BCA)
Synonym(s):
LPL, Phospholipase A1, Diacylglycerol acylhydrolase, Diacylglycerol lipase
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
bovine milk
Quality Level
form
ammonium sulfate suspension
specific activity
≥2,000 units/mg protein (BCA)
storage temp.
2-8°C
General description
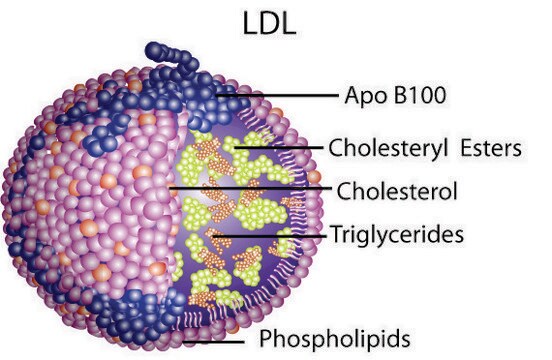
Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) from bovine milk is a glycoprotein. It exists as a homodimer and comprises two N-linked oligosaccharides. It is heat-labile.Lipoprotein lipase is an enzyme found on the surface of vascular endothelial cells, where it is anchored to capillary walls. It is mainly present in adipose tissue, heart, and muscle tissue. It is synthesized by extrahepatic tissues, particularly adipocytes, and the gene encoding the protein is situated on chromosome 8p22.
Application
- as a supplement to test its effect on DiI (1,1′-dioctadecyl-3,3,3′-tetramethyl-indocarbocyanine perchlorate)- very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) uptake in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells.
- to treat human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs) for the lipolysis of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TGRL).
- to test its effect on gene expression in normal human astrocytes.
- in primary hepatocyte isolation and lipoprotein binding to identify Sulf2 inhibition in T2DM mice for improving diabetic dyslipidemia.
- in transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β1) immunoassay to test if the TGF-β signaling system regulates the up-regulation and activation of activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) in human aortic endothelial cells (HAEC) induced by lipolysis products.
- in human TGRL isolation.
- in in vitro lipolysis assay with HSPG-bound LPL, to investigate the effect of human apoE2 (Lys146→Gln) on lipoprotein metabolism.
- in hydrolysis of triglycerides.
- in developing in vitro model of gastrointestinal digestion to investigate the effects of chlorophyll on lipid digestion.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Unit Definition
Physical form
Preparation Note
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
The potential for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease through increased dietary intake of omega-3 (w-3) fish oils is not a recent scientific discovery.
Lipid Induced Insulin Resistance
Instructions for working with enzymes supplied as ammonium sulfate suspensions
Protocols
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) hydrolyzes triglycerides associated with VLDL.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service