CLS431751
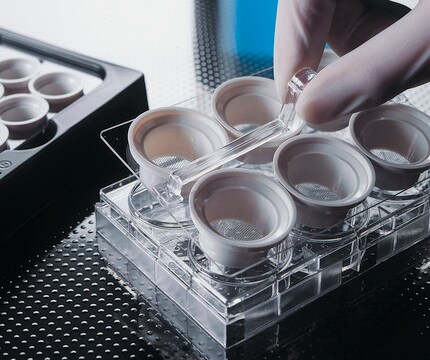
Corning® cell strainer
pore size 70 μm, white, sterile, pkg of (individually wrapped), pack of 50 ea, Corning 431751
Synonym(s):
Cell Strainer
About This Item
Recommended Products
material
Nylon
white
sterility
sterile
packaging
pack of 50 ea
pkg of (individually wrapped)
manufacturer/tradename
Corning 431751
pore size
70 μm
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- Single cell suspensions of blood cells from marrow, pancreas, thymus, tonsil, and lymph nodes
- Stem cells, tissue-derived cells, and cancer cells
- Preparation of specimens for primary cell cultures and immunogens
- Preparation of freezing stocks
- Filtering agglutinative proteins produced in inactivation serum
Features and Benefits
- Strong nylon mesh with 70- micron pores for optimal performance in a variety of applications
- Evenly spaced mesh pores providing consistent and reliable results
- Conveniently accessible in individual packaging
- Extended lip on strainer enables aseptic handling with forceps
- Molded color-coded polypropylene frame with tab enables easy handling and identification
- Fits all major brands of 50mL conical tubes
- Disposable, easy-to-use, inexpensive, maintains sample integrity
- Sterilized by γ−irradiation, noncytotoxic
Legal Information
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Development of a novel serum-free and xeno-free human mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) osteocyte differentiation media.
Organoid culture products to generate tissue and stem cell derived 3D brain, intestinal, gut, lung and cancer tumor organoid models.
Protocols
Information about mesenchyme, specifically mesenchymal stem cell procotols. Step-by-step cell culture protocols for mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) isolation, expansion and differentiation.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service