04497
Phalloidin–Atto 665
suitable for fluorescence, ≥90% (HPLC)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352116
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥90% (HPLC)
manufacturer/tradename
ATTO-TEC GmbH
fluorescence
λex 663 nm; λem 684 nm in 0.1 M phosphate pH 7.0
suitability
suitable for fluorescence
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Atto 665 Phalloidin is a new fluorescent label closely related to Atto 647N. As such the dye shows an extraordinarily high fluorescence quantum yield, excellent thermal and photo-stability, outstanding ozone resistance, and very little triplet formation. Atto 665 Phalloidin is a cationic dye (charge +1). In common with most Atto-labels, absorption and fluorescence are independent of pH in the range of 2 to 11, used in typical applications.
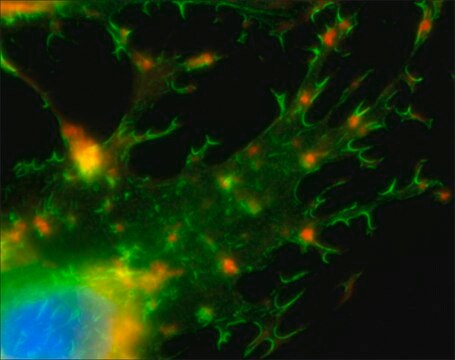
Phalloidin is a fungal toxin isolated from the poisonous mushroom Amanita phalloides. Its toxicity is attributed to the ability to bind F actin in liver and muscle cells. As a result of binding phalloidin, actin filaments become strongly stabilized. Phalloidin has been found to bind only to polymeric and oligomeric forms of actin, and not to monomeric actin. The dissociation constant of the actin-phalloidin complex has been determined to be on the order of 3 x 10-8. Phalloidin differs from amanitin in rapidity of action; at high dose levels, death of mice or rats occurs within 1 or 2 hours. Fluorescent conjugates of phalloidin are used to label actin filaments for histological applications. Some structural features of phalloidin are required for the binding to actin. However, the side chain of amino acid 7 (g-d-dihydroxyleucine) is accessible for chemical modifications without appreciable loss of affinity for actin.
find more information here
Phalloidin is a fungal toxin isolated from the poisonous mushroom Amanita phalloides. Its toxicity is attributed to the ability to bind F actin in liver and muscle cells. As a result of binding phalloidin, actin filaments become strongly stabilized. Phalloidin has been found to bind only to polymeric and oligomeric forms of actin, and not to monomeric actin. The dissociation constant of the actin-phalloidin complex has been determined to be on the order of 3 x 10-8. Phalloidin differs from amanitin in rapidity of action; at high dose levels, death of mice or rats occurs within 1 or 2 hours. Fluorescent conjugates of phalloidin are used to label actin filaments for histological applications. Some structural features of phalloidin are required for the binding to actin. However, the side chain of amino acid 7 (g-d-dihydroxyleucine) is accessible for chemical modifications without appreciable loss of affinity for actin.
find more information here
Legal Information
This product is for Research use only. In case of intended commercialization, please contact the IP-holder (ATTO-TEC GmbH, Germany) for licensing.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service