Linkers for Fmoc SPPS
Novabiochem® has one of the most extensive ranges of linkers and derivatized resins for Fmoc solid phase peptide synthesis. The properties of these resins are summarized in Table 1, together with links to the appropriate loading and cleavage protocols.
Peptide acids
For the synthesis of peptide acids, benzyl alcohol-type linkers such as Wang or HMPA are used. Special consideration must be given to peptides containing Cys, His, Gly, Pro, Met and Trp residues at the C-terminus. Esterification of Cys and His to these linkers is always problematic, as these amino acids are extremely prone to enantiomerize under the rather forcing conditions used. For preparing such peptides, resins derivatized with trityl-type linkers, such as NovaSyn® TGT resin, NovaPEG Trt or 2-chlorotrityl resin, should be used because loading these supports does not necessitate activation of the Fmoc-amino acid carboxyl group and so is completely free from racemization and dipeptide formation. Trityl-based resins are also strongly recommended for the preparation of peptides containing C-terminal Gly, Pro, Met and Trp residues. Glycine- and proline-containing dipeptides attached to benzyl alcohol-based linkers are prone to undergo diketopiperazine formation during Fmoc deprotection, with loss of peptide chains from the support, whereas Met and Trp residues can be alkylated by the cations generated at the linker during the cleavage reaction, resulting in reattachment of the peptide to the support. In both instances, these side reactions are reduced, if not eliminated, with trityl resins, owing to the bulk of the linker.
Novabiochem® product range also offers the convenience of pre-loaded Wang and NovaSyn® TGA resins. The bulk resin used to prepare our pre-loaded Wang resins is synthesis tested, to ensure consistent and reliable performance in synthesis. The major impurities arising from loading of the amino acid, such as dipeptide content and racemization, are also determined.
Protected peptide acids
Resins derivatized with trityl-type linkers, such as NovaSyn® TGT resin, NovaPEG Trt or 2-chlorotrityl resin, provide the simplest approach to the synthesis of protected peptide acids. Treatment with 20% TFE in DCM releases fully protected peptide acids, with negligible loss of side-chain protecting groups provided Fmoc-His(Clt)-OH is employed for introduction of His residues. After evaporation of the solvent, the product is isolated by precipitation with water.
We also provide NovaSyn® TGT resin, NovaPEG Trt and 2-chlorotrityl resins pre-loaded with the first amino acid residue.
Peptide amides
Resins based on the Fmoc-Rink Amide linker, such as Rink Amide AM or Rink Amide MBHA, are recommended for routine synthesis of peptide amides. Loading of the C-terminal residue can be affected using any standard coupling method. Peptide amides are released by treatment with 95% TFA cleavage cocktails.
Protected peptide amides
Sieber Amide resin offers the most practical route to protected peptide amides. The C-terminal amino acid is loaded on the resin using standard coupling methods. Treatment with 1% TFA in DCM releases the protected peptide amide.
Peptide N-alkyamides
The simplest approach involves reductive amination of the appropriate primary amine to FIA AM resin, to generate a resin-bound secondary amine. Acylation of this group with the C-terminal residue of the peptide, chain extension, and TFA cleavage, affords the peptide N-alkylamide. For peptide N-methyl- and N-ethylamide, FIA-AM resins are available pre-derivatized with methylamine and ethylamine.
Peptide alcohols
We offer 2-chlorotrityl resin pre-loaded with glycinol and theoninol. These resins enable the direct synthesis of peptide alcohols containing these residues at the C-terminus. For peptides containing other C-terminal amino alcohols, the use of resins derivatized with the HMBA linker is recommended. Peptides attached to this linker are cleaved by reduction with NaBH4 as peptide alcohols.
Peptide aldehydes
A small range of aldehydes derived from amino acids pre-loaded on Thr-Gly-NovaSyn® resin are available. Following side-chain deprotection with TFA, peptide aldehydes are released by treatment with acetic acid/water/DCM/MeOH. Peptide aldehydes may also by prepared by reductive cleavage from Weinreb AM resin. For larger scale synthesis, oxidation of protected peptide alcohols with IBX or Dess-Martin reagent in solution provides the most effective method
Peptide esters
Small scale synthesis of peptide methyl esters can be achieved by methanolysis of peptides attached to the HMBA linker. However, the yields are often poor and the products contaminated with peptide acid. One very effective scaleable method involves the reaction of the protected peptide acid with TMS diazomethane in MeOH. For synthesis of other esters, use of the BAL approach involving anchoring of a pre-formed amino-acid ester to a formyl resin is recommended.
Peptide thioesters
Small scale synthesis of peptide thioesters can be achieved by thioloysis from sulfamylbutyryl and Dbz linkers. For larger quantities coupling of a protected peptide acid to a pre-formed amino acid thioester, followed by side-chain deprotection is recommended.
Linkers for Fmoc SPPS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resin | Cleavage | Loading protocol | Cleavage protocol | |
Peptide acid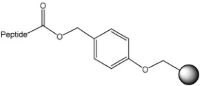 | Wang resin NovaSyn® TGA resin HMPA-PEGA resin HMPA-NovaGel™ NovaPEG Wang resin (4-Bromomethyl) phenoxy-methyl polystyrene | 95% TFA | Method 2: Attachment to hydroxymethyl resins using symmetrical anhydride Method 3: Attachment to hydroxymethyl resins using MSNT/MeIm | Method 2: General TFA cleavage |
Protected peptide acid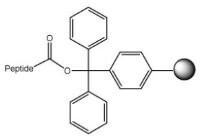 | 2-Chlorotrityl resin NovaSyn® TGT alcohol resin | 1% TFA in DCM, AcOH/DCM/TFE, 20% TFE in DCM | Method 5: Loading of trityl resins | Method5: Cleavage with dilute TFA Method 6: Cleavage with TFE/DCM |
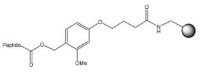 | HMPB-MBHA resin NovaPEG HMPB resin | 1% TFA in DCM | Method 2: Attachment to hydroxymethyl resins using symmetrical anhydride Method 3: Attachment to hydroxymethyl resins using MSNT/MeIm | Method 5: Cleavage with dilute TFA |
Peptide carboxamide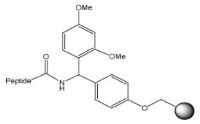 | NovaSyn® TGR resin Fmoc-PAL AM resin PAL-NovaPEG/NovaSyn® TG resin Ramage Amide AM resin Rink Amide resin Rink Amide AM/MBHA resin Rink Amide NovaGel™/ PEGA resin NovaPEG Rink Amide resin | 95% TFA | Method 4: Attachment of carboxylic acids to amino resins | Method 2: General TFA cleavage |
Protected peptide carboxamide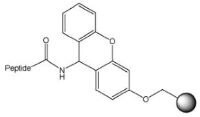 | Sieber Amide resin NovaSyn® TG Sieber resin | 1% TFA in DCM | Method 4: Attachment of carboxylic acids to amino resins | Method 5: Cleavage with dilute TFA |
Peptide N-alkylamide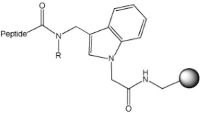 | Methyl indole AM resin FIA AM resin Ethyl indole AM resins | 95% TFA | Method 4: Attachment of carboxylic acids to amino resins | Method 2: General TFA cleavage |
Peptide ester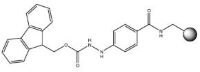 | 4-Fmoc-hydrazinobenzoyl AM NovaGel™ | Cu(OAc)2, ROH, pyridine | Method 4: Attachment of carboxylic acids to amino resins | Method 13: Oxidative cleavage of hydrazinobenzoyl resins |
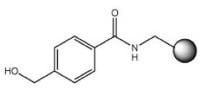 | HMBA-AM resin HMBA-NovaGel™ HMBA-PEGA resin | ROH/DIPEA/DMF | Method 2: Attachment to hydroxymethyl resins using symmetrical anhydride Method 3: Attachment to hydroxymethyl resins using MSNT/MeIm | Method 10: Cleavage with methanol/DIPEA to give the methyl ester |
Peptide thioester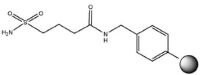 | 4-Sulfamylbutyryl AM resin and others | i)TMS-CHN2 ii)RSH | Method 8: Loading of sulfamyl resins | Method 12: Thioester ligation with sulfamyl resins |
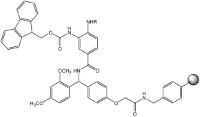 | Dawson Dbz AM resin MeDdz NovaSyn® TGR resin | i)p-NO2PhOCOCl ii)DIPEA iii)TFA | Method 7: Loading of Dbz resins | Method 14: Thioester ligation with Dawson Dbz AM resin |
Peptide hydrazide | HMBA-AM resin, HMBA-NovaGel™ HMBA-PEGA resin | NH2NH2/DMF | Method 2: Attachment to hydroxymethyl resins using symmetrical anhydride Method 3: Attachment to hydroxymethyl resins using MSNT/MeIm | Method 13: Oxidative cleavage of hydrazinobenzoyl resins |
Peptide alcohols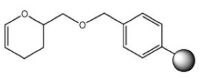 | DHP HM | 95% TFA | Method 9: Loading DHP HM resin | Method 2: General TFA cleavage |
 | HMBA-AM resin HMBA-NovaGel™ HMBA-PEGA resin | NaBH4/EtOH | Method 2: Attachment to hydroxymethyl resins using symmetrical anhydride Method 3: Attachment to hydroxymethyl resins using MSNT/MeIm | Method 11: Cleavage with borohydride to give the peptide alcohol |
Peptide aldehydes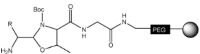 | H-Aaa-H NovaSyn® TG resin | AcOH/water/ DCM/MeOH (10:5:63:21) | Method 10: Loading of H-Thr-Gly-NovaSyn® TG resin | Method 16: Cleavage of H-Thr-Gly-NovaSyn® TG resin. |
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?