L5263
Lyticase from Arthrobacter luteus
partially purified powder, ≥1,500 units/mg protein
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
partially purified powder
specific activity
≥1,500 units/mg protein
composition
Protein, ≥10% biuret
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Biochem/physiol Actions
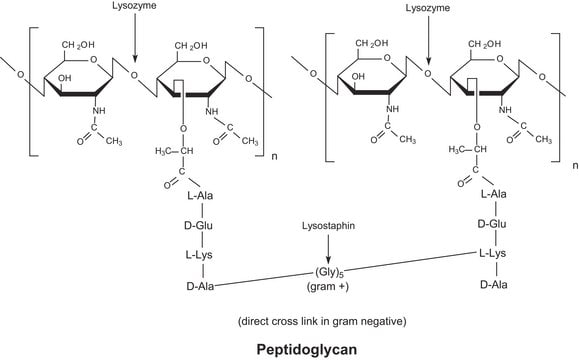
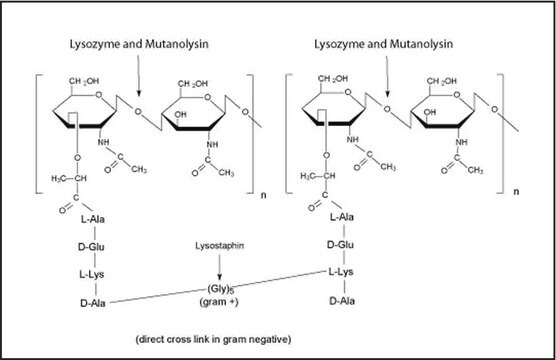
Lyticase hydrolyzes poly-β(1→3)-glucose such as yeast cell wall glucan.
Unit Definition
One unit will produce a ΔA800 of 0.001 per min at pH 7.5 at 25 °C, using a suspension of yeast as substrate in a 3 mL reaction mixture.
Physical form
Partially purified powder containing ammonium sulfate and stabilizer
Other Notes
View more information on enzymes for complex carbohydrate analysis at www.sigma-aldrich.com/enzymeexplorer
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Sanford J Silverman et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(15), 6946-6951 (2010-03-26)
Oscillations in patterns of expression of a large fraction of yeast genes are associated with the "metabolic cycle," usually seen only in prestarved, continuous cultures of yeast. We used FISH of mRNA in individual cells to test the hypothesis that
Construction of chromosome-specific libraries of yeast artificial chromosome recombinants from somatic hybrid cell lines.
B Arveiler
Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 29, 379-402 (1994-01-01)
B N Doebbeling et al.
Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, 16(3), 377-383 (1993-03-01)
Candida species are important nosocomial pathogens, particularly in immunocompromised and critically ill patients. A variety of methods have been used to differentiate strains, but an optimal system has not been established. We compared methods for typing a panel of nine
Physical mapping by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis.
J Maule
Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 68, 93-121 (1997-01-01)
Markus M M Bisschops et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1864(1), 231-242 (2016-11-08)
Non-dividing Saccharomyces cerevisiae cultures are highly relevant for fundamental and applied studies. However, cultivation conditions in which non-dividing cells retain substantial metabolic activity are lacking. Unlike stationary-phase (SP) batch cultures, the current experimental paradigm for non-dividing yeast cultures, cultivation under
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service