C9972
Cholera Toxin B subunit
biotin conjugate, lyophilized powder
Synonym(s):
CTB
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
conjugate
biotin conjugate
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
mol wt
~12 kDa
composition
Protein, ~40% Lowry
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
CCOc1ccccc1C(=O)Nc2ccc(Cl)c(c2)C(F)(F)F
InChI
1S/C16H13ClF3NO2/c1-2-23-14-6-4-3-5-11(14)15(22)21-10-7-8-13(17)12(9-10)16(18,19)20/h3-9H,2H2,1H3,(H,21,22)
InChI key
YDXZSNHARVUYNM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Cholera Toxin B (CTB) is secreted by Vibrio cholerae. CTB functions as an oral subunit vaccine for cholera, which is associated with acute watery diarrhoea. It acts as a mucosal immunogen. Cholera toxin (CT) stimulates cell surface molecules, such as antigen presenting cells (APCs), murine and human dendritic cells (DCs). CT also has immunomodulatory properties. It induces the secretion of interleukin 1 (IL-1) from macrophages and enhances their APC function.
Application
Cholera Toxin B subunit has been used:
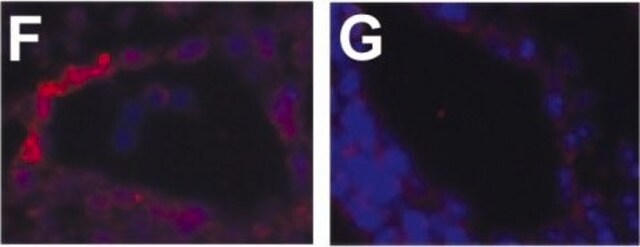
- in immunofluorescence
- in the analysis of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II lipid raft partitioning
- in live cell three-dimensional tracking of SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells
- to assess the toll-like receptors (TLR) and FcRγ (Fc receptor γ chain) – CARD9 (caspase recruitment domain family member 9) activation by cholera Toxin B (CTB)
Biochem/physiol Actions
The cholera toxin B subunit is used for track tracing in neurological research, taking advantage of GM1 ganglioside binding and retrograde transport.
The cholera toxin B subunit is used for track tracing in neurological research, taking advantage of GM1 ganglioside binding and retrograde transport. Tissue culture cells treated with cholera toxin are not killed and tissues of animals do not become necrotic.
Quality
Biotin content ~1.0 mole/mole protein.
Physical form
Lyophilized powder containing sodium phosphate buffer salts, sodium azide and sodium EDTA.
Analysis Note
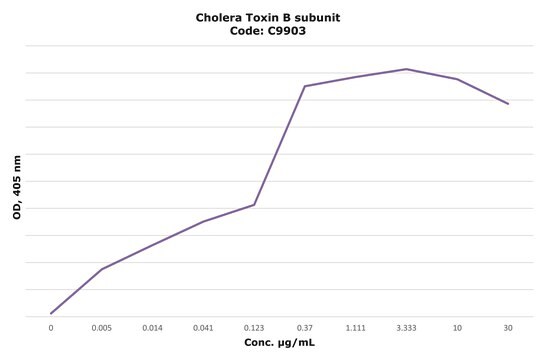
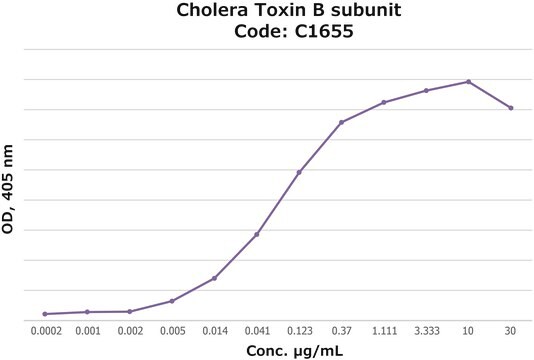
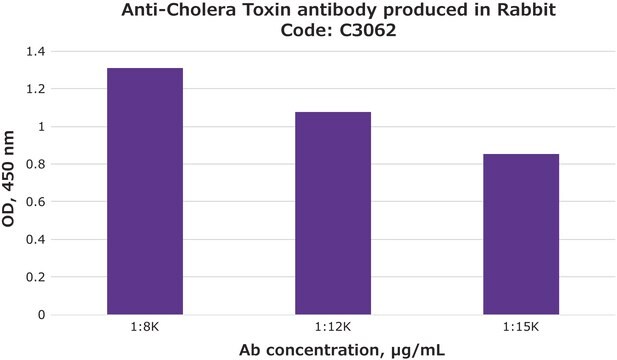
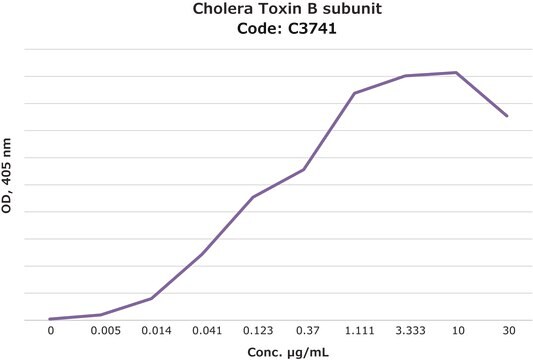
Activity measured by ELISA using ganglioside GM1-coated multiwell plates, rabbit anti-Cholera toxin B subunit, and peroxidase-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG as the secondary antibody. 50% saturation of binding is achieved with 0.02-1 μg of Cholera toxin B subunit-biotin conjugate per mL. The conjugated B subunit gives a similar value for 50% binding to that of unconjugated B subunit from which it is prepared.
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 3
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
3D tracking of single nanoparticles and quantum dots in living cells by out-of-focus imaging with diffraction pattern recognition
Gardini L, et al.
Scientific Reports, 5, 16088-16088 (2015)
Evidence for TLR4 and FcRgamma-CARD9 activation by cholera toxin B subunit and its direct bindings to TREM2 and LMIR5 receptors
Phongsisay V, et al.
Molecular Immunology, 66(2), 463-471 (2015)
The Ia. 2 epitope defines a subset of lipid raft-resident MHC class II molecules crucial to effective antigen presentation
Busman-Sahay K, et al.
Journal of Immunology, 1100336-1100336 (2011)
Expression of the native cholera toxin B subunit gene and assembly as functional oligomers in transgenic tobacco chloroplasts1
Daniell H, et al.
Journal of Molecular Biology, 311(5), 1001-1009 (2001)
Eva Koffeman et al.
Methods in molecular medicine, 136, 69-86 (2007-11-07)
T-cells specific for a particular antigen represent a small percentage of the overall T-cell population. Detecting the presence of antigen specific T-cells in patients, animal models or populations of cultured cells has presented a challenge to researchers. The T-cell capture
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service