17944
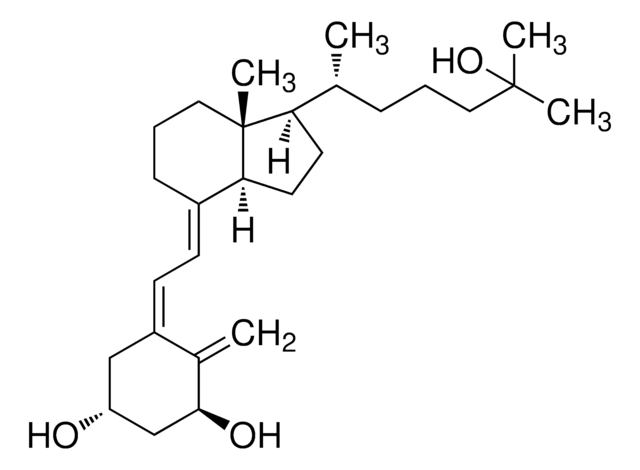
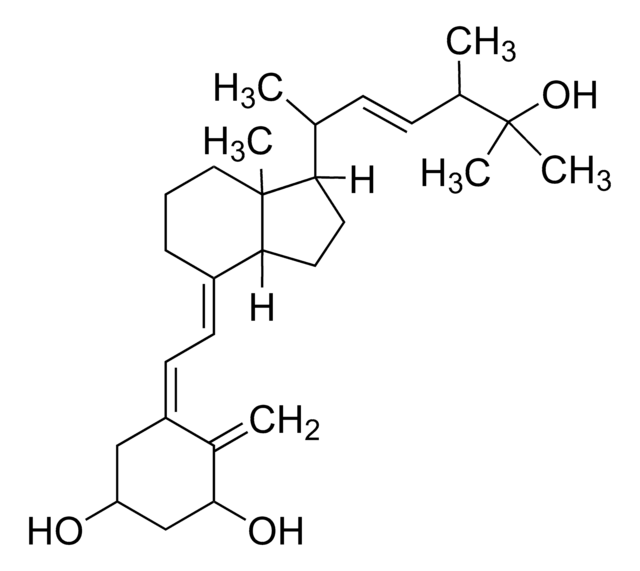
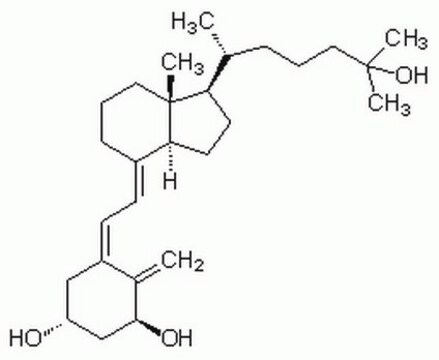
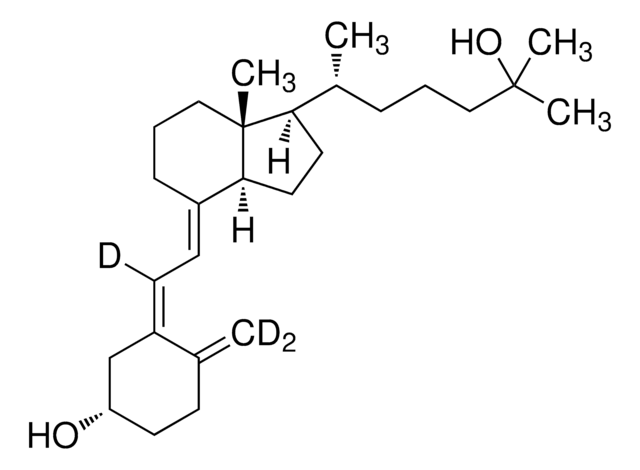
1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D2
≥97.0% (sum of vitamin and previtamin, HPLC)
Synonym(s):
1α,25-Dihydroxycalciferol
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
synthetic
Quality Level
Assay
≥97.0% (sum of vitamin and previtamin, HPLC)
form
crystals
color
white to light yellow
storage temp.
−70°C
SMILES string
C[C@H](\C=C\[C@H](C)C(C)(C)O)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2\C(CCC[C@]12C)=C\C=C3\C[C@@H](O)C[C@H](O)C3=C
InChI
1S/C28H44O3/c1-18(9-10-19(2)27(4,5)31)24-13-14-25-21(8-7-15-28(24,25)6)11-12-22-16-23(29)17-26(30)20(22)3/h9-12,18-19,23-26,29-31H,3,7-8,13-17H2,1-2,4-6H3/b10-9+,21-11+,22-12-/t18-,19+,23-,24-,25+,26+,28-/m1/s1
InChI key
ZGLHBRQAEXKACO-XJRQOBMKSA-N
Biochem/physiol Actions
Packaging
related product
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 2 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - STOT RE 1 Oral
Storage Class Code
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) is naturally synthesized from ergosterol by invertebrates, fungi, and plants in response to ultraviolet B irradiation, while vitamin D3 synthesis (cholecalciferol) is uniquely initiated in the skin of vertebrates. During sun exposure, ultraviolet B photons are absorbed by 7-dehydrocholesterol, which is found within the plasma membranes of epidermal and dermal skin layers. This reaction yields an unstable derivative of 7-dehydrocholesterol, named precholecalcitrol, which rapidly rearranges to vitamin D3. Vitamin D binding protein (DBP) is a carrier protein responsible for drawing vitamin D3 from the plasma membrane into the dermal capillaries within the extracellular space.
This application shows an Ascentis Express F5 provided rapid resolution of the isobaric vitamin D metabolites. MS detection provides the necessary secondary resolution.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service