328251
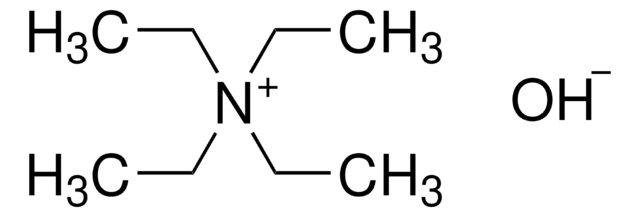
Tetramethylammonium hydroxide solution
10 wt. % in H2O
Synonym(s):
N,N,N-trimethyl-methanaminium hydroxide, TMAH, TMAOH
About This Item
Recommended Products
vapor pressure
17.5 mmHg ( 20 °C)
Quality Level
concentration
10 wt. % in H2O
refractive index
n20/D 1.3521
density
1.006 g/mL at 25 °C
functional group
amine
SMILES string
[OH-].C[N+](C)(C)C
InChI
1S/C4H12N.H2O/c1-5(2,3)4;/h1-4H3;1H2/q+1;/p-1
InChI key
WGTYBPLFGIVFAS-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- A reactant to synthesize epoxy-polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (EPOSS) via sol-gel method using 2-(3,4-epoxycyclohexyl)ethyltrimethoxysilane (ECTMS) in IPA.
- An ionic liquid to modify SnO2 nanocrystals, which are applicable as an efficient electron transport layer in perovskite solar cells.
TMAH can also be used as an anisotropic etchant for silicon due to its high silicon etching rate. The main advantage of using TMAH is that it causes no danger to electrical circuits due to the absence of alkali ions.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 1 Dermal - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 3 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B - STOT RE 1 Dermal - STOT SE 1
Target Organs
Central nervous system, Liver,thymus
Storage Class Code
6.1B - Non-combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service