860462P
Avanti
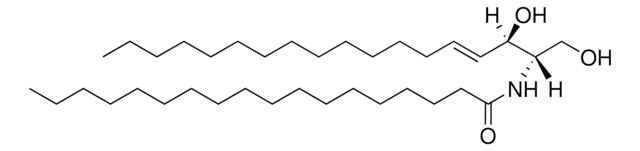
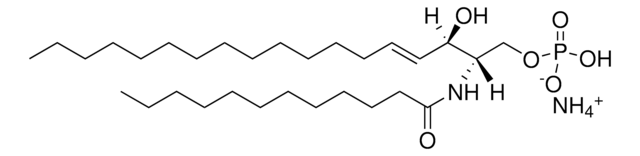
N-C16-deoxysphinganine
N-palmitoyl-1-deoxysphinganine (m18:0/16:0), powder
Synonym(s):
N-hexadecanoyl-1-deoxysphinganine (m18:0/16:0); N-C16-1-deoxyDHCer; 110960
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C34H69NO2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
523.92
UNSPSC Code:
12352211
NACRES:
NA.25
Recommended Products
Assay
>99% (TLC)
form
powder
packaging
pkg of 1 × 1 mg (860462P-1mg)
pkg of 1 × 5 mg (860462P-5mg)
manufacturer/tradename
Avanti Polar Lipids 860462P
lipid type
sphingolipids
bioactive lipids
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Commonly referred to as 1-deoxydihydroceramide (1-deoxyDHCer), this product is the N-acylated form of 1-deoxysphinganine, a potent inhibitor of sphingolipid metabolism. The biological activity of 1-deoxyDHCer is not clearly understood at this time.
N-C16-deoxysphinganine Commonly referred to as 1-deoxydihydroceramide (1-deoxyDHCer), is the N-acylated form of 1-deoxysphinganine, a potent inhibitor of sphingolipid metabolism. The N-acyl group can be 16, 20 and 24 carbon chain. N-acylsphinganines (dihydroceramides) are synthesized by the acylation of sphingoid bases in the presence of ceramide synthases (CerS).
Biochem/physiol Actions
N-acylsphinganines (dihydroceramides) levels are lower during ceramide synthase inhibition. They are intermediates of ceramide and dihydrosphingolipids synthesis. Treatment of MCF7 cancer cells with fenretinide alters sphingolipid metabolism.
Packaging
5 mL Amber Glass Screw Cap Vial (860462P-1mg)
5 mL Amber Glass Screw Cap Vial (860462P-5mg)
Legal Information
Avanti Research is a trademark of Avanti Polar Lipids, LLC
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Sphingolipidomics: a valuable tool for understanding the roles of sphingolipids in biology and disease
Merrill AH, et al.
Journal of Lipid Research, 50, S97-S102 (2009)
Ceramide synthase inhibition by fumonisin B1 causes accumulation of 1-deoxysphinganine a novel category of bioactive 1-deoxysphingoid bases and 1-deoxydihydroceramides biosynthesized by mammalian cell lines and animals
Zitomer NC, et al.
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284(8), 4786-4795 (2009)
Thematic Review Series: Sphingolipids. Biodiversity of sphingoid bases (?sphingosines?) and related amino alcohols
Pruett ST, et al.
Journal of Lipid Research, 49(8), 1621-1639 (2008)
Noemi Jiménez-Rojo et al.
Biophysical journal, 107(12), 2850-2859 (2014-12-18)
Ceramides and dihydroceramides are N-acyl derivatives of sphingosine and sphinganine, respectively, which are the major sphingoid-base backbones of mammals. Recent studies have found that mammals, like certain other organisms, also produce 1-deoxy-(dihydro)ceramides (1-deoxyDHCers) that contain sphingoid bases lacking the 1-hydroxyl-
Sarah T Pruett et al.
Journal of lipid research, 49(8), 1621-1639 (2008-05-24)
"Sphingosin" was first described by J. L. W. Thudichum in 1884 and structurally characterized as 2S,3R,4E-2-aminooctadec-4-ene-1,3-diol in 1947 by Herb Carter, who also proposed the designation of "lipides derived from sphingosine as sphingolipides." This category of amino alcohols is now
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service